Regulation of zinc homeostasis by inducible NO synthase-derived NO: nuclear metallothionein translocation and intranuclear Zn2+ release
- PMID: 14617770
- PMCID: PMC283527
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2335190100
Regulation of zinc homeostasis by inducible NO synthase-derived NO: nuclear metallothionein translocation and intranuclear Zn2+ release
Abstract
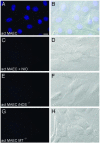
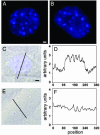
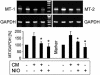
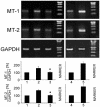
Zn2+ is critical for the functional and structural integrity of cells and contributes to a number of important processes including gene expression. It has been shown that NO exogenously applied via NO donors resulting in nitrosative stress leads to cytoplasmic Zn2+ release from the zinc storing protein metallothionein (MT) and probably other proteins that complex Zn2+ via cysteine thiols. We show here that, in cytokine-activated murine aortic endothelial cells, NO derived from the inducible NO synthase (iNOS) induces a transient nuclear release of Zn2+. This nuclear Zn2+ release depends on the presence of MT as shown by the lack of this effect in activated endothelial cells from MT-deficient mice and temporally correlates with nuclear MT translocation. Data also show that NO is an essential but not sufficient signal for MT-mediated Zn2+ trafficking from the cytoplasm into the nucleus. In addition, we found that, endogenously via iNOS, synthesized NO increases the constitutive mRNA expression of both MT-1 and MT-2 genes and that nitrosative stress exogenously applied via an NO donor increases constitutive MT mRNA expression via intracellular Zn2+ release. In conclusion, we here provide evidence for a signaling mechanism based on iNOS-derived NO through the regulation of intracellular Zn2+ trafficking and homeostasis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide-induced nuclear translocation of the metal responsive transcription factor, MTF-1 is mediated by zinc release from metallothionein.Vascul Pharmacol. 2006 Mar;44(3):149-55. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2005.10.004. Epub 2006 Jan 19. Vascul Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16423564
-
Nitric oxide-induced changes in intracellular zinc homeostasis are mediated by metallothionein/thionein.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002 Feb;282(2):L185-92. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00267.2001. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11792622
-
Cysteine-Zn2+ complexes: unique molecular switches for inducible nitric oxide synthase-derived NO.FASEB J. 2001 Nov;15(13):2503-7. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0240hyp. FASEB J. 2001. PMID: 11689476
-
Balance between metallothionein and metal response element binding transcription factor 1 is mediated by zinc ions (review).Mol Med Rep. 2015 Mar;11(3):1582-6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2969. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25405524 Review.
-
Metallothionein as a negative regulator of pulmonary inflammation.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2013;14(4):414-9. doi: 10.2174/1389201011314040005. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23590139 Review.
Cited by
-
Metallothionein (MT) -I and MT-II expression are induced and cause zinc sequestration in the liver after brain injury.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031185. Epub 2012 Feb 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363575 Free PMC article.
-
Metallothioneins 1 and 2 Modulate Inflammation and Support Remodeling in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy in Mice.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:7174127. doi: 10.1155/2016/7174127. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27403038 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and Transcriptional Responses in Weaned Piglets Fed Diets with Varying Phosphorus and Calcium Levels.Nutrients. 2019 Feb 20;11(2):436. doi: 10.3390/nu11020436. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30791512 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-leishmanial effects of trinitroglycerin in BALB/C mice infected with Leishmania major via nitric oxide pathway.Korean J Parasitol. 2009 Jun;47(2):109-15. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2009.47.2.109. Epub 2009 May 27. Korean J Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19488416 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc-gene interaction related to inflammatory/immune response in ageing.Genes Nutr. 2008 Jul;3(2):61-75. doi: 10.1007/s12263-008-0085-2. Genes Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18850188 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

