Simulation of the folding equilibrium of alpha-helical peptides: a comparison of the generalized Born approximation with explicit solvent
- PMID: 14617775
- PMCID: PMC283524
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2232868100
Simulation of the folding equilibrium of alpha-helical peptides: a comparison of the generalized Born approximation with explicit solvent
Abstract
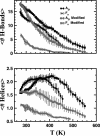
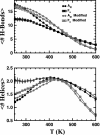
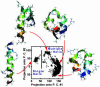
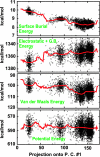
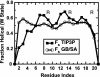
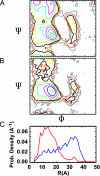
We compare simulations using the generalized Born/surface area (GB/SA) implicit solvent model with simulations using explicit solvent (transferable intermolecular potential 3 point, TIP3P) to test the GB/SA algorithm. We use the replica exchange molecular dynamics method to sample the conformational phase space of two alpha-helical peptides, A21 and the Fs, by using two different classical potentials and both water models. We find that when using GB/SA: (i) A21 is predicted to be more helical than the Fs peptide at all temperatures; (ii) the native structure of the Fs peptide is predicted to be a helical bundle instead of a single helix; and (iii) the persistence length and most probable end-to-end distance are too large in the unfolded state when compared against the explicit solvent simulations. We find that the potential of mean force in the phi(psi) plane is markedly different in the two solvents, making the two simulated peptides respond differently when the backbone torsions are perturbed. A fit of the temperature melting curves obtained in these simulations to a Lifson-Roig model finds that the GB/SA model has an unphysically large nucleation parameter, whereas the explicit solvent model produces values similar to experiment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Free energy landscape of protein folding in water: explicit vs. implicit solvent.Proteins. 2003 Nov 1;53(2):148-61. doi: 10.1002/prot.10483. Proteins. 2003. PMID: 14517967
-
Secondary structure bias in generalized Born solvent models: comparison of conformational ensembles and free energy of solvent polarization from explicit and implicit solvation.J Phys Chem B. 2007 Feb 22;111(7):1846-57. doi: 10.1021/jp066831u. Epub 2007 Jan 27. J Phys Chem B. 2007. PMID: 17256983 Free PMC article.
-
Can a continuum solvent model reproduce the free energy landscape of a beta -hairpin folding in water?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 1;99(20):12777-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.142430099. Epub 2002 Sep 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12242327 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in implicit solvent-based methods for biomolecular simulations.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Apr;18(2):140-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.01.003. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 18304802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide folding simulations.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003 Apr;13(2):168-74. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(03)00040-x. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 12727509 Review.
Cited by
-
ABSINTH: a new continuum solvation model for simulations of polypeptides in aqueous solutions.J Comput Chem. 2009 Apr 15;30(5):673-99. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21005. J Comput Chem. 2009. PMID: 18506808 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic pathways of beta-hairpin (un)folding in explicit solvent.Biophys J. 2005 Jan;88(1):50-61. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.048744. Epub 2004 Oct 29. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15516524 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium perchlorate effects on the helical stability of a mainly alanine peptide.Biophys J. 2010 Jan 20;98(2):186-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.10.013. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20338840 Free PMC article.
-
Electrostatic solvation energy for two oppositely charged ions in a solvated protein system: salt bridges can stabilize proteins.Biophys J. 2010 Feb 3;98(3):470-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.10.031. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20141761 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion maps, clustering and fuzzy Markov modeling in peptide folding transitions.J Chem Phys. 2014 Sep 21;141(11):114102. doi: 10.1063/1.4893963. J Chem Phys. 2014. PMID: 25240340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Still, W., Tempczyk, A., Hawley, R. & Hendrickson, T. (1990) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 6127–6129.
-
- Rapp, C. & Friesner, R. (1999) Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 35, 173–183. - PubMed
-
- Wang, T. & Wade, R. (2003) Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 50, 158–169. - PubMed
-
- Morozov, A., Kortemme, T. & Baker, D. (2003) J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 2075–2090.
-
- Onufriev, A., Case, D. & Bashford, D. (2002) J. Comput. Chem. 23, 1297–1304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

