Mycobacterium tuberculosis phagosome maturation arrest: mycobacterial phosphatidylinositol analog phosphatidylinositol mannoside stimulates early endosomal fusion
- PMID: 14617817
- PMCID: PMC329390
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-05-0307
Mycobacterium tuberculosis phagosome maturation arrest: mycobacterial phosphatidylinositol analog phosphatidylinositol mannoside stimulates early endosomal fusion
Abstract
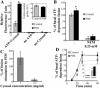
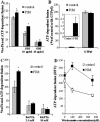
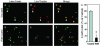
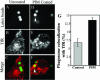
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a facultative intracellular pathogen that parasitizes macrophages by modulating properties of the Mycobacterium-containing phagosome. Mycobacterial phagosomes do not fuse with late endosomal/lysosomal organelles but retain access to early endosomal contents by an unknown mechanism. We have previously reported that mycobacterial phosphatidylinositol analog lipoarabinomannan (LAM) blocks a trans-Golgi network-to-phagosome phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway. In this work, we extend our investigations of the effects of mycobacterial phosphoinositides on host membrane trafficking. We present data demonstrating that phosphatidylinositol mannoside (PIM) specifically stimulated homotypic fusion of early endosomes in an ATP-, cytosol-, and N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor-dependent manner. The fusion showed absolute requirement for small Rab GTPases, and the stimulatory effect of PIM increased upon partial depletion of membrane Rabs with RabGDI. We found that stimulation of early endosomal fusion by PIM was higher when phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase was inhibited by wortmannin. PIM also stimulated in vitro fusion between model phagosomes and early endosomes. Finally, PIM displayed in vivo effects in macrophages by increasing accumulation of plasma membrane-endosomal syntaxin 4 and transferrin receptor on PIM-coated latex bead phagosomes. In addition, inhibition of phagosomal acidification was detected with PIM-coated beads. The effects of PIM, along with the previously reported action of LAM, suggest that M. tuberculosis has evolved a two-prong strategy to modify its intracellular niche: its products block acquisition of late endosomal/lysosomal constituents, while facilitating fusion with early endosomal compartments.
Figures




References
-
- Anderson, R.J., and Roberts, E.G. (1930). The chemistry of lipoids of tubercule bacilli. J. Biol. Chem. 89, 611-611.
-
- Ballou, C.E., and Lee, Y.C. (1964). The structure of myoinositol mannoside from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry 72, 682-685. - PubMed
-
- Band, A.M., Ali, H., Vartiainen, M.K., Welti, S., Lappalainen, P., Olkkonen, V.M., and Kuismanen, E. (2002). Endogenous plasma membrane t-SNARE syntaxin 4 is present in rab11 positive endosomal membranes and associates with cortical actin cytoskeleton. FEBS Lett. 531, 513-519. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri, M.A., Hoffenberg, S., Roberts, R., Mukhopadhyay, A., Pomrehn, A., Dickey, B.F., and Stahl, P.D. (1998). Evidence for a symmetrical requirement for Rab5-GTP in in vitro endosome-endosome fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 25850-25855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

