Pharmacokinetics and plasma concentrations of acetylsalicylic acid after intravenous, rectal, and intragastric administration to horses
- PMID: 14620867
- PMCID: PMC280715
Pharmacokinetics and plasma concentrations of acetylsalicylic acid after intravenous, rectal, and intragastric administration to horses
Abstract
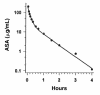
Six healthy adult horses (5 mares and 1 stallion) were given a single dose of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), 20 mg/kg of body weight, by intravenous (IV), rectal, and intragastric (IG) routes. Serial blood samples were collected via jugular venipuncture over a 36-h period, and plasma ASA and salicylic acid (SA) concentrations were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. After IV administration, the mean elimination rate constant of ASA (+/- the standard error of the mean) was 1.32 +/- 0.09 h(-1), the mean elimination half-life was 0.53 +/- 0.04 h, the area under the plasma concentration-versus-time curve (AUC) was 2555 +/- 98 microg x min/mL, the plasma clearance was 472 +/- 18.9 mL/h/kg, and the volume of distribution at steady state was 0.22 +/- 0.01 L/kg. After rectal administration, the plasma concentration of ASA peaked at 5.05 +/- 0.80 microg/mL at 0.33 h, then decreased to undetectable levels by 4 h; the plasma concentration of SA peaked at 17.39 +/- 5.46 microg/mL at 2 h, then decreased to 1.92 +/- 0.25 microg/mL by 36 h. After rectal administration, the AUC for ASA was 439.4 +/- 94.55 microg x min/mL and the bioavailability was 0.17 +/- 0.037. After IG administration, the plasma concentration of ASA peaked at 1.26 +/- 0.10 microg/mL at 0.67 h, then declined to 0.37 +/- 0.37 microg/mL by 36 h; the plasma concentration of SA peaked at 23.90 +/- 4.94 microg/mL at 4 h and decreased to 0.85 +/- 0.31 microg/mL by 36 h. After IG administration, the AUC for ASA was 146.70 +/- 24.90 microg x min/mL and the bioavailability was 0.059 +/- 0.013. Administration of a single rectal dose of ASA of 20 mg/kg to horses results in higher peak plasma ASA concentrations and greater bioavailability than the same dose given IG. Plasma ASA concentrations after rectal administration should be sufficient to inhibit platelet thromboxane production, and doses lower than those suggested for IG administration may be adequate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum concentrations and pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin after intravenous and intragastric administration to mares.Can J Vet Res. 2000 Jul;64(3):171-7. Can J Vet Res. 2000. PMID: 10935883 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics of multiple-dose administration of eltenac in horses.Am J Vet Res. 1998 Nov;59(11):1447-50. Am J Vet Res. 1998. PMID: 9829405
-
Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of nimesulide in goats.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Apr;30(2):157-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2007.00838.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17348902
-
Relative bioavailability of rapidly dispersing, plain, and microencapsuled acetylsalicylic acid tablets after single dose administration.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1998 Mar;36(3):133-8. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1998. PMID: 9562228 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics of rectal drug administration, Part II. Clinical applications of peripherally acting drugs, and conclusions.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1991 Aug;21(2):110-28. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199121020-00003. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1991. PMID: 1884566 Review.
Cited by
-
Synovial distribution of "systemically" administered acetylsalicylic acid in the isolated perfused equine distal limb.BMC Vet Res. 2013 Mar 26;9:56. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-9-56. BMC Vet Res. 2013. PMID: 23531229 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-sectional study of the availability and pharmacist's knowledge of nano-pharmaceutical drugs in Palestinian hospitals.BMC Health Serv Res. 2018 Apr 5;18(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-3060-7. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018. PMID: 29622013 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Development of Low- and Medium-Viscosity Alginate Beads Loaded with Pluronic® F-127 Nanomicelles.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jun 29;16(13):4715. doi: 10.3390/ma16134715. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37445029 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and in vitro efficacy of salicylic acid after oral administration of acetylsalicylic acid in horses.BMC Vet Res. 2017 Jan 19;13(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12917-017-0955-1. BMC Vet Res. 2017. PMID: 28103874 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of acetylsalicylic acid after intravenous and oral administration to healthy volunteers.Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Mar 19;6:51-9. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S47895. eCollection 2014. Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24672263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cham BE, Ross-Lee L, Bochner F, Imhoff DM. Measurement and pharmacokinetics of acetylsalicylic acid by a novel high performance liquid chromatographic assay. Ther Drug Monit 1980;2:365–371. - PubMed
-
- Muir N, Nichols JD, Clifford JM, Stillings MR, Hoare RC. The influence of dosage form on aspirin kinetics: implications for cardiovascular use. Curr Med Res Opin 1997;13:547–553. - PubMed
-
- Kanto J, Klossner J, Mantyla R, Yrjana T. Bioavailability of rectal aspirin in neurosurgical patients. Acta Anaesth Scand 1981;75:25–26. - PubMed
-
- Gingerich DA, Baggot JD, Yeary RA. Pharmacokinetics and dosage of aspirin in cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc 1975;167:945–948. - PubMed
-
- Davis LE. Clinical pharmacology of salicylates. J Am Vet Med Assoc 1980;176:65–66. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources