Role of beta-catenin in synaptic vesicle localization and presynaptic assembly
- PMID: 14622577
- PMCID: PMC2757419
- DOI: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00718-9
Role of beta-catenin in synaptic vesicle localization and presynaptic assembly
Abstract
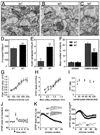
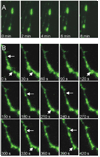
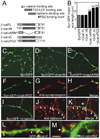
Cadherins and catenins are thought to promote adhesion between pre and postsynaptic elements in the brain. Here we show a role for beta-catenin in localizing the reserved pool of vesicles at presynaptic sites. Deletion of beta-catenin in hippocampal pyramidal neurons in vivo resulted in a reduction in the number of reserved pool vesicles per synapse and an impaired response to prolonged repetitive stimulation. This corresponded to a dispersion of vesicles along the axon in cultured neurons. Interestingly, these effects are not due to beta-catenin's involvement in cadherin-mediated adhesion or wnt signaling. Instead, beta-catenin modulates vesicle localization via its PDZ binding domain to recruit PDZ proteins such as Veli to cadherin at synapses. This study defines a specific role for cadherins and catenins in synapse organization beyond their roles in mediating cell adhesion.
Figures




References
-
- Ahmari SE, Buchanan J, Smith SJ. Assembly of presynaptic active zones from cytoplasmic transport packets. Nat. Neurosci. 2000;3:445–451. - PubMed
-
- Barth AI, Nathke IS, Nelson WJ. Cadherins, catenins and APC protein: interplay between cytoskeletal complexes and signaling pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997;9:683–690. - PubMed
-
- Bozdagi O, Shan W, Tanaka H, Benson DL, Huntley GW. Increasing numbers of synaptic puncta during late-phase LTP: N-cadherin is synthesized, recruited to synaptic sites, and required for potentiation. Neuron. 2000;28:245–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

