The Cl(-) channel blocker niflumic acid releases Ca(2+) from an intracellular store in rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 14623766
- PMCID: PMC1574157
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705571
The Cl(-) channel blocker niflumic acid releases Ca(2+) from an intracellular store in rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells
Abstract
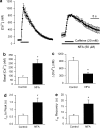
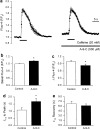
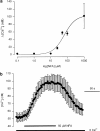
The effect of the Cl- channel blockers niflumic acid (NFA), 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)-benzoic acid (NPPB), 4,4'-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid (DIDS), and anthracene-9-carboxylic acid (A-9-C), on Ca2+ signalling in rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells was examined. Intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) was monitored with either fura-2 or fluo-4, and caffeine was used to activate the ryanodine receptor, thereby releasing Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). NFA and NPPB significantly increased basal [Ca2+]i and attenuated the caffeine-induced increase in [Ca2+]i. These Cl- channel blockers also increased the half-time (t1/2) to peak for the caffeine-induced [Ca2+]i transient, and slowed the removal of Ca2+ from the cytosol following application of caffeine. Since DIDS and A-9-C were found to adversely affect fura-2 fluorescence, fluo-4 was used to monitor intracellular Ca2+ in studies involving these Cl- channel blockers. Both DIDS and A-9-C increased basal fluo-4 fluorescence, indicating an increase in intracellular Ca2+, and while DIDS had no significant effect on the t1/2 to peak for the caffeine-induced Ca2+ transient, it was significantly increased by A-9-C. In the absence of extracellular Ca2+, NFA significantly increased basal [Ca2+]i, suggesting that the release of Ca2+ from an intracellular store was responsible for the observed effect. Depleting the SR with the combination of caffeine and cyclopiazonic acid prevented the increase in basal [Ca2+]i induced by NFA. Additionally, incubating the cells with ryanodine also prevented the increase in basal [Ca2+]i induced by NFA. These data show that Cl- channel blockers have marked effects on Ca2+ signalling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Furthermore, examination of the NFA-induced increase in [Ca2+]i indicates that it is likely due to Ca2+ release from an intracellular store, most probably the SR.
Figures




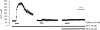
Similar articles
-
Dual effect of blocking agents on Ca2+-activated Cl(-) currents in rabbit pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.J Physiol. 2002 Feb 15;539(Pt 1):119-31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013270. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11850506 Free PMC article.
-
Chloride ion currents contribute functionally to norepinephrine-induced vascular contraction.Am J Physiol. 1998 Jul;275(1):H151-60. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1998.275.1.H151. Am J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9688908
-
Relaxation of endothelin-1-induced pulmonary arterial constriction by niflumic acid and NPPB: mechanism(s) independent of chloride channel block.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Mar;288(3):1242-50. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999. PMID: 10027865
-
[The effects of chloride channel blockers on thrombocytic cytoplasmic free calcium concentration and platelet aggregation].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Mar;26(3):170-4. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15946532 Chinese.
-
Ca2+-activated Cl- current in retinal arteriolar smooth muscle.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Jan;50(1):364-71. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2524. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 18775864 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
NSAIDs modulate GABA-activated currents via Ca2+-activated Cl- channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons.Exp Ther Med. 2016 May;11(5):1755-1761. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3158. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27168798 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of new-generation TMEM16A inhibitors on calcium-activated chloride currents in rabbit urethral interstitial cells of Cajal.Pflugers Arch. 2017 Nov;469(11):1443-1455. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2028-5. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 28733893
-
ANO1 channels are expressed in mouse urethral smooth muscle but do not contribute to agonist or neurally evoked contractions.Sci Rep. 2025 May 19;15(1):17365. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00953-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40389459 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the rat gastric slow-wave conduction pathway: bridging in vitro and in vivo methods, revealing a loosely coupled region in the distal stomach.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024 Aug 1;327(2):G254-G266. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00069.2024. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38860855 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic-nucleotide-gated cation current and Ca2+-activated Cl current elicited by odorant in vertebrate olfactory receptor neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Oct 4;113(40):11078-11087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1613891113. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27647918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BRAYDEN D.J., KROUSE M.E., LAW T., WINE J.J. Stilbenes stimulate T84 Cl− secretion by elevating Ca2+ Am. J. Physiol. 1993;264:G325–G333. - PubMed
-
- CABANTCHIK A.I., ROTHSTEIN A. Membrane proteins related to anion permeability of human red blood cells. I. Localization of disulfonic stilbene binding sites in proteins involved in permeation. J. Membr. Biol. 1974;15:207–226. - PubMed
-
- CHIPPERFIELD A.R., HARPER A.A. Chloride in smooth muscle. Progr. Biophys. Molec. Biol. 2000;74:175–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

