Autoregulation of E-cadherin expression by cadherin-cadherin interactions: the roles of beta-catenin signaling, Slug, and MAPK
- PMID: 14623871
- PMCID: PMC2173691
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200308162
Autoregulation of E-cadherin expression by cadherin-cadherin interactions: the roles of beta-catenin signaling, Slug, and MAPK
Abstract
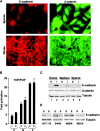
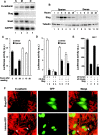
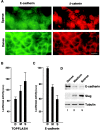
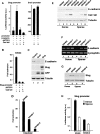
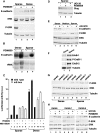
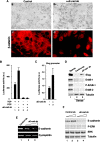
Transcriptional repression of E-cadherin, characteristic of epithelial to mesenchymal transition, is often found also during tumor cell invasion. At metastases, migratory fibroblasts sometimes revert to an epithelial phenotype, by a process involving regulation of the E-cadherin-beta-catenin complex. We investigated the molecular basis of this regulation, using human colon cancer cells with aberrantly activated beta-catenin signaling. Sparse cultures mimicked invasive tumor cells, displaying low levels of E-cadherin due to transcriptional repression of E-cadherin by Slug. Slug was induced by beta-catenin signaling and, independently, by ERK. Dense cultures resembled a differentiated epithelium with high levels of E-cadherin and beta-catenin in adherens junctions. In such cells, beta-catenin signaling, ErbB-1/2 levels, and ERK activation were reduced and Slug was undetectable. Disruption of E-cadherin-mediated contacts resulted in nuclear localization and signaling by beta-catenin, induction of Slug and inhibition of E-cadherin transcription, without changes in ErbB-1/2 and ERK activation. This autoregulation of E-cadherin by cell-cell adhesion involving Slug, beta-catenin and ERK could be important in tumorigenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Barker, N., and H. Clevers. 2001. Tumor environment: a potent driving force in colorectal cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 7:535–537. - PubMed
-
- Batlle, E., E. Sancho, C. Franci, D. Dominguez, M. Monfar, J. Baulida, and A. Garcia De Herreros. 2000. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:84–89. - PubMed
-
- Batlle, E., J.T. Henderson, H. Beghtel, M.M. van den Born, E. Sancho, G. Huls, J. Meeldijk, J. Robertson, M. van de Wetering, T. Pawson, and H. Clevers. 2002. β-Catenin and TCF mediate cell positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the expression of EphB/ephrinB. Cell. 111:251–263. - PubMed
-
- Behrens, J., U. Frixen, J. Schipper, M. Weidner, and W. Birchmeier. 1992. Cell adhesion in invasion and metastasis. Semin. Cell Biol. 3:169–178. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ze'ev, A., and B. Geiger. 1998. Differential molecular interactions of β-catenin and plakoglobin in adhesion, signaling and cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10:629–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

