Tumor rejection by modulation of tumor stromal fibroblasts
- PMID: 14623905
- PMCID: PMC2194119
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030849
Tumor rejection by modulation of tumor stromal fibroblasts
Abstract
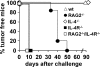
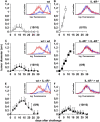
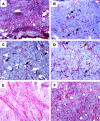
Interleukin (IL)-4-secreting tumors are rejected in mice, an effect that is thought to be immune mediated. However, solid tumors are embedded in a stroma that often contains tumor-promoting fibroblasts, a cell population whose function is also affected by IL-4. Here we show that IL-4-secreting tumors grew undiminished in IL-4 receptor (R)-deficient (IL-4R-/-) mice. In IL-4R+/+ mice they were long-term suppressed in the absence of T cells but complete rejection required T cells, compatible with the assumption that hematopoietic cells needed to respond to IL-4. Surprisingly, bone marrow (BM) chimeric mice revealed that IL-4R expression exclusively on non-BM-derived cells was sufficient for tumor rejection. Fibroblasts in the tumor stroma were identified as a target cell type for IL-4 because they accumulated in IL-4-secreting tumors and displayed an activated phenotype. Additionally, coinjection of IL-4R+/+ but not IL-4R-/- fibroblasts was sufficient for the rejection of IL-4-secreting tumors in IL-4R-/- mice. Our data demonstrate a novel mechanism by which IL-4 contributes to tumor rejection and show that the targeted modulation of tumor-associated fibroblasts can be sufficient for tumor rejection.
Figures
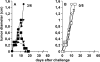
References
-
- Tepper, R.I., P.K. Pattengale, and P. Leder. 1989. Murine interleukin-4 displays potent anti-tumor activity in vivo. Cell. 57:503–512. - PubMed
-
- Blankenstein, T., S. Cayeux, and Z. Qin. 1996. Genetic approaches to cancer immunotherapy. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 129:1–49. - PubMed
-
- Musiani, P., A. Modesti, M. Giovarelli, F. Cavallo, M.P. Colombo, P.L. Lollini, and G. Forni. 1997. Cytokines, tumour-cell death and immunogenicity: a question of choice. Immunol. Today. 18:32–36. - PubMed
-
- Noffz, G., Z. Qin, M. Kopf, and T. Blankenstein. 1998. Neutrophils but not eosinophils are involved in growth suppression of IL-4-secreting tumors. J. Immunol. 160:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Golumbek, P.T., A.J. Lazenby, H.I. Levitsky, L.M. Jaffee, H. Karasuyama, M. Baker, and D.M. Pardoll. 1991. Treatment of established renal cancer by tumor cells engineered to secrete interleukin-4. Science. 254:713–716. - PubMed

