Hepatoprotection by the farnesoid X receptor agonist GW4064 in rat models of intra- and extrahepatic cholestasis
- PMID: 14623915
- PMCID: PMC281645
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI18945
Hepatoprotection by the farnesoid X receptor agonist GW4064 in rat models of intra- and extrahepatic cholestasis
Abstract
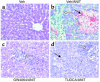
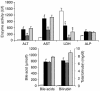
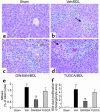
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is a bile acid-activated transcription factor that is a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily. Fxr-null mice exhibit a phenotype similar to Byler disease, an inherited cholestatic liver disorder. In the liver, activation of FXR induces transcription of transporter genes involved in promoting bile acid clearance and represses genes involved in bile acid biosynthesis. We investigated whether the synthetic FXR agonist GW4064 could protect against cholestatic liver damage in rat models of extrahepatic and intrahepatic cholestasis. In the bile duct-ligation and alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate models of cholestasis, GW4064 treatment resulted in significant reductions in serum alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and lactate dehydrogenase, as well as other markers of liver damage. Rats that received GW4064 treatment also had decreased incidence and extent of necrosis, decreased inflammatory cell infiltration, and decreased bile duct proliferation. Analysis of gene expression in livers from GW4064-treated cholestatic rats revealed decreased expression of bile acid biosynthetic genes and increased expression of genes involved in bile acid transport, including the phospholipid flippase MDR2. The hepatoprotection seen in these animal models by the synthetic FXR agonist suggests FXR agonists may be useful in the treatment of cholestatic liver disease.
Figures



Comment in
-
The nuclear bile acid receptor FXR as a novel therapeutic target in cholestatic liver diseases: hype or hope?Hepatology. 2004 Jul;40(1):260-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.20294. Hepatology. 2004. PMID: 15239110 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bull LN, et al. A gene encoding a P-type ATPase mutated in two forms of hereditary cholestasis. Nat. Genet. 1998;18:219–224. - PubMed
-
- Strautnieks SS, et al. A gene encoding a liver-specific ABC transporter is mutated in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat. Genet. 1998;20:233–238. - PubMed
-
- Smit JJ, et al. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell. 1993;75:451–462. - PubMed
-
- Paumgartner G, Beuers U. Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestatic liver disease: mechanisms of action and therapeutic use revisited. Hepatology. 2002;36:525–531. - PubMed

