Identification, characterization, and gene expression profiling of endotoxin-induced myocarditis
- PMID: 14623955
- PMCID: PMC283576
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2336220100
Identification, characterization, and gene expression profiling of endotoxin-induced myocarditis
Abstract
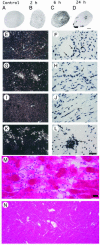
In septic shock, reversible cardiac dysfunction starts within 24 h. Myocardial depressant factors are thought to cause myocyte dysfunction, resulting in alterations of intrinsic cardiac function. Nitric oxide is a myocardial depressant factor candidate. Here we identify endotoxin-induced myocarditis (EIM) a previously uncharacterized pathophysiological entity. Features of EIM include differential patterns of inducible NO synthase (NOS2) mRNA induction in the left (LV) and right (RV) ventricles during the systemic response inflammatory syndrome (SIRS) and the presence of myocarditis with focal areas of aseptic necrosis in the RV 24 h after SIRS induction. Even though clinical data lead to the presumption of myocardial injury in sepsis, the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms have not been previously elucidated. Gene expression profiling was used to test the hypothesis of differential LV and RV responses in EIM, and revealed novel patterns of qualitative and quantitative expansion of transcription. Those genes are novel targets for drug development in SIRS and sepsis. Our results demonstrate spatial and temporal heterogeneity of myocardial responses in EIM. These findings justify the design of treatments to ameliorate tissue injury in the RV. Because the complexity of the inflammatory response increases substantially as time elapses, we suggest a stepwise and multitarget therapeutic approach for SIRS and sepsis. Our findings can help identify innate immune pathways that could become targets for immunotherapy in the treatment of disease caused by potential bioterrorism agents.
Figures




References
-
- Wong, M.-L., Rettori, V., Al-Shekhlee, A., Bongiorno, P. B., Canteros, G., McCann, S. M., Gold, P. W. & Licinio, J. (1996) Nat. Med. 2, 581-584. - PubMed
-
- Libert, C. (2003) Nature 421, 328-329. - PubMed
-
- Bone, R. C. (1992) J. Am. Med. Assoc. 268, 3452-3455.
-
- Dennhardt, R., Gramm, H. J., Meinhold, K. & Voigt, K. (1989) Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 308, 751-756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR017611/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR00865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K12 RR017611/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HG002500/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK063240/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR016996/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MH062777/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DK063240/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM061394/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR017365/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL004526/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HG002500/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM061394/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 RR016996/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058851/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K30 HL004526/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 RR017365/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK058851/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

