Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: fabrication methods and transport studies
- PMID: 14623977
- PMCID: PMC283494
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2331316100
Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: fabrication methods and transport studies
Abstract
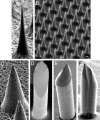
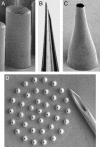
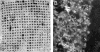
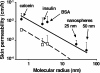
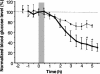
Arrays of micrometer-scale needles could be used to deliver drugs, proteins, and particles across skin in a minimally invasive manner. We therefore developed microfabrication techniques for silicon, metal, and biodegradable polymer microneedle arrays having solid and hollow bores with tapered and beveled tips and feature sizes from 1 to 1,000 microm. When solid microneedles were used, skin permeability was increased in vitro by orders of magnitude for macromolecules and particles up to 50 nm in radius. Intracellular delivery of molecules into viable cells was also achieved with high efficiency. Hollow microneedles permitted flow of microliter quantities into skin in vivo, including microinjection of insulin to reduce blood glucose levels in diabetic rats.
Figures
References
-
- Madou, M. (1997) Fundamentals of Microfabrication (CRC, Boca Raton, FL).
-
- Chen, J. & Wise, K. D. (1997) IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 44, 760–769. - PubMed
-
- Brazzle, J., Papautsky, I. & Frazier, A. B. (1999) IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 18, 53–58. - PubMed
-
- Lin, L. & Pisano, A. P. (1999) IEEE J. Micromech. Syst. 8, 78–84.
-
- Stoeber, B. & Liepmann, D. (2000) Proc. ASME MEMS Dev. 2000 IMECE 2, 355–359.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

