Intraarterial administration of Abciximab for thromboembolic events occurring during aneurysm coil placement
- PMID: 14625229
- PMCID: PMC8148902
Intraarterial administration of Abciximab for thromboembolic events occurring during aneurysm coil placement
Abstract
Background and purpose: Platelet-derived thrombi may occur during intracranial aneurysm coiling. We report a series of 13 patients treated with intraarterial Abciximab for thrombus formation complicating aneurysm coiling.
Methods: Four patients were treated for acutely ruptured aneurysms. Three procedures consisted of the retreatment of previously coiled aneurysms. Six patients had asymptomatic untreated aneurysms. Abciximab was administered intraarterially through a microcatheter as a bolus of 4-10 mg over a period of 10-20 minutes. All patients underwent postthrombolysis control angiography. They also underwent immediate pre- and postoperative cranial CT.
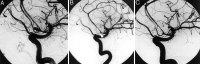
Results: In 10/13 cases, the thrombi developed without coil protrusion into the parent artery. In one case, the thrombus was generated from the guiding catheter and embolized remote from the aneurysm site. In one case, the thrombus developed before any coil placement. In another patient, a coil loop protruded into the parent artery favoring a heightened thrombotic state. Arterial thrombi were totally occlusive in two patients, whereas in the remaining 11 cases, the thrombi were not totally obstructive. Complete recanalization was achieved in 92% (12/13) of cases within 20-30 minutes. Incomplete arterial reopening was noted in one case, in which a thrombus fragment embolized distally, causing cerebral infarction. There were no Abciximab-related intracranial hemorrhages.
Conclusion: Intraarterial Abciximab was effective in this series for the treatment of thrombotic complications occurring during aneurysm coiling.
Figures

References
-
- Eskridge JM, Song JK. Endovascular embolization of 150 basilar tip aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils: results of the Food and Drug Administration multicenter clinical trial. J Neurosurg 1998;89:81–86 - PubMed
-
- McDougall CG, Halbach VV, Dowd CF, et al. Endovascular treatment of basilar tip aneurysms using electrolytically detachable coils. J Neurosurg 1996;84:393–399 - PubMed
-
- Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Mawad M. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of acute intracranial aneurysm: perioperative anatomical and clinical outcome in 403 patients. J Neurosurg 1997;86:475–482 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
