NK cells in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation
- PMID: 14627124
- PMCID: PMC11034224
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-003-0378-7
NK cells in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation
Abstract
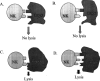
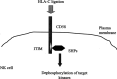
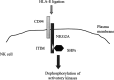
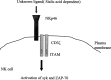
NK cells, until recently an ignored subset of lymphocytes, have begun to emerge as important cytotoxic effectors. It is now accepted that NK cells together with T cells constitute major actors in graft-versus-leukemia reaction after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT). Over the last several years the mechanisms regulating the activation of NK cells have been the subject of intense investigations encouraged by the clinical implications that these studies will have. This article provides a general overview of NK-cells biology and regulation pertinent to their function in allogeneic BMT, followed by a review of the in vivo preclinical and clinical evidence for the beneficial effect of NK cells in the adoptive immunotherapy of leukemia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
VLA-6 (CDw49f) is an important adhesion molecule in NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity following autologous or allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.Exp Hematol. 1995 Dec;23(14):1530-4. Exp Hematol. 1995. PMID: 8542943
-
Suppression of graft-versus-host disease and amplification of graft-versus-tumor effects by activated natural killer cells after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.J Clin Invest. 1998 May 1;101(9):1835-42. doi: 10.1172/JCI1268. J Clin Invest. 1998. PMID: 9576746 Free PMC article.
-
NK-cell purging of leukemia: superior antitumor effects of NK cells H2 allogeneic to the tumor and augmentation with inhibitory receptor blockade.Blood. 2003 Dec 1;102(12):4067-75. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-04-1367. Epub 2003 Jul 31. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12893752
-
Immunobiology of natural killer cells and bone marrow transplantation: merging of basic and preclinical studies.Immunol Rev. 2001 Jun;181:279-89. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1810124.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11513149 Review.
-
The potential role of NK cells in the separation of graft-versus-tumor effects from graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.Immunol Rev. 1997 Jun;157:167-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1997.tb00981.x. Immunol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9255629 Review.
Cited by
-
T cell-mediated graft-versus-leukemia reactions after allogeneic stem cell transplantation.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005 Nov;54(11):1043-58. doi: 10.1007/s00262-005-0681-6. Epub 2005 May 11. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005. PMID: 15887014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone marrow deficient in IFN-{gamma} signaling selectively reverses GVHD-associated immunosuppression and enhances a tumor-specific GVT effect.Blood. 2009 May 14;113(20):5002-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-11-187385. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19258593 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of natural killer cell receptor-expressing cells in immunotherapy for leukemia.Int J Hematol. 2005 Jan;81(1):6-12. doi: 10.1532/ijh97.04152. Int J Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15717681 Review.
-
Expression and function of immune ligand-receptor pairs in NK cells and cancer stem cells: therapeutic implications.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018 Apr;41(2):107-121. doi: 10.1007/s13402-018-0373-9. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018. PMID: 29470831 Review.
References
-
- Bensussan Eur Cytokine Netw. 1998;9:577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

