Selective reactions of cutaneous and muscle afferent neurons to peripheral nerve transection in rats
- PMID: 14627640
- PMCID: PMC6740909
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-33-10559.2003
Selective reactions of cutaneous and muscle afferent neurons to peripheral nerve transection in rats
Abstract
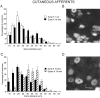
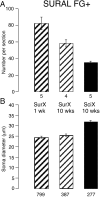
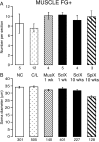
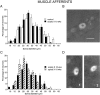
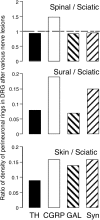
To determine whether peripheral nerve injury has similar effects on all functional types of afferent neuron, we retrogradely labeled populations of neurons projecting to skin and to muscle with FluoroGold and lesioned various peripheral nerves in the rat. Labeled neurons were counted after different periods and related to immunohistochemically identified ectopic terminals and satellite cells in lumbar dorsal root ganglia. After 10 weeks, 30% of cutaneous afferent somata labeled from transected sural nerves had disappeared but, if all other branches of the sciatic nerve had also been cut, 60% of cutaneous neurons were lost. Small-diameter sural neurons preferentially disappeared. In contrast, the number of muscle afferent somata was not affected by transection of various nerves. p75 was downregulated in axotomized cutaneous neurons but in not axotomized muscle neurons. Conversely, p75 was upregulated in satellite cells around cutaneous but not muscle neurons. Consistent with this, perineuronal rings containing tyrosine hydroxylase, calcitonin gene-related peptide, galanin, or synaptophysin were formed preferentially around cutaneous neurons. Selective lesions of predominantly cutaneous nerves triggered the formation of rings, but none were detected after selective lesions of muscle nerves. We conclude that cutaneous neurons are both more vulnerable and more associated with ectopic nerve terminals than muscle neurons in dorsal root ganglia after transection and ligation of peripheral nerves.
Figures



References
-
- Aldskogius H, Risling M ( 1981) Effects of sciatic neurectomy on neuronal numbers and size distribution in the L7 ganglion of the kitten. Exp Neurol 74: 597-604. - PubMed
-
- Baron R, Jänig W, Kollmann W ( 1988) Sympathetic and afferent somata projecting in hindlimb nerves and the anatomical organization of the lumbar sympathetic nervous system of the rat. J Comp Neurol 275: 460-468. - PubMed
-
- Ferri CC, Ghasemlou N, Bisby MA, Kawaja MD ( 2002) Nerve growth factor alters p75 neurotrophin receptor-induced effects in mouse facial motoneurons following axotomy. Brain Res 950: 180-185. - PubMed
-
- Fields HL, Rowbotham M, Baron R ( 1998) Postherpetic neuralgia: irritable nociceptors and deafferentation. Neurobiol Dis 5: 209-227. - PubMed
-
- Groves MJ, Christopherson T, Giometto B, Scaravilli F ( 1997) Axotomy-induced apoptosis in adult rat primary sensory neurons. J Neurocytol 26: 615-624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
