Critical role of dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus in a wide range of behavioral circadian rhythms
- PMID: 14627654
- PMCID: PMC6740926
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-33-10691.2003
Critical role of dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus in a wide range of behavioral circadian rhythms
Abstract
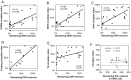
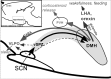
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) contains the brain's circadian pacemaker, but mechanisms by which it controls circadian rhythms of sleep and related behaviors are poorly understood. Previous anatomic evidence has implicated the dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus (DMH) in circadian control of sleep, but this hypothesis remains untested. We now show that excitotoxic lesions of the DMH reduce circadian rhythms of wakefulness, feeding, locomotor activity, and serum corticosteroid levels by 78-89% while also reducing their overall daily levels. We also show that the DMH receives both direct and indirect SCN inputs and sends a mainly GABAergic projection to the sleep-promoting ventrolateral preoptic nucleus, and a mainly glutamate-thyrotropin-releasing hormone projection to the wake-promoting lateral hypothalamic area, including orexin (hypocretin) neurons. Through these pathways, the DMH may influence a wide range of behavioral circadian rhythms.
Figures




References
-
- Abrahamson EE, Leak RK, Moore RY ( 2001) The suprachiasmatic nucleus projects to posterior hypothalamic arousal systems. NeuroReport 12: 435-440. - PubMed
-
- Alfoldi P, Franken P, Tobler I, Borbely AA ( 1991) Short light-dark cycles influence sleep stages and EEG power spectra in the rat. Behav Brain Res 43: 125-131. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Price JL ( 1983) An air pressure system for the injection of tracer substances into the brain. J Neurosci Methods 9: 35-43. - PubMed
-
- Antonio Martinez J, Vargas ML, Fuente T, Del Rio Garcia J, Milanes MV ( 1990) Plasma beta-endorphin and cortisol levels in morphine-tolerant rats and in naloxone-induced withdrawal. Eur J Pharmacol 182: 117-123. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Chen S, Zhu Y, Oshinsky ML ( 2001) A neural circuit for circadian regulation of arousal. Nat Neurosci 4: 732-738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
