The Frog Prince: a reconstructed transposon from Rana pipiens with high transpositional activity in vertebrate cells
- PMID: 14627820
- PMCID: PMC290277
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg910
The Frog Prince: a reconstructed transposon from Rana pipiens with high transpositional activity in vertebrate cells
Abstract
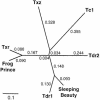
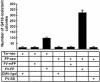
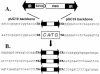
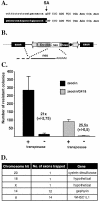
Members of the Tc1/mariner superfamily of transposable elements isolated from vertebrates are transpositionally inactive due to the accumulation of mutations in their transposase genes. A novel open reading frame-trapping method was used to isolate uninterrupted transposase coding regions from the genome of the frog species Rana pipiens. The isolated clones were approximately 90% identical to a predicted transposase gene sequence from Xenopus laevis, but contained an unpredicted, approximately 180 bp region encoding the N-terminus of the putative transposase. None of these native genes was found to be active. Therefore, a consensus sequence of the transposase gene was derived. This engineered transposase and the transposon inverted repeats together constitute the components of a novel transposon system that we named Frog Prince (FP). FP has only approximately 50% sequence similarity to Sleeping Beauty (SB), and catalyzes efficient cut-and-paste transposition in fish, amphibian and mammalian cell lines. We demonstrate high-efficiency gene trapping in human cells using FP transposition. FP is the most efficient DNA-based transposon from vertebrates described to date, and shows approximately 70% higher activity in zebrafish cells than SB. Frog Prince can greatly extend our possibilities for genetic analyses in vertebrates.
Figures


References
-
- Driever W., Solnica-Krezel,L., Schier,A., Neuhauss,S., Maliki,J., Stemple,D., Stainier,D., Zwartkruis,F., Abdelilah,S., Rangini,Z., Belak,J. and Boggs,C. (1996) A genetic screen for mutations affecting embryogenesis in zebrafish. Development, 123, 37–46. - PubMed
-
- Haffter P., Granato,M., Brand,M., Mullins,M.C., Hammerschmidt,M., Kane,D.A., Odenthal,J., van Eeden,F.J., Jiang,Y.J., Heisenberg,C.P., Kelsh,R.N., Furutani-Seiki,M., Vogelsang,E., Beuchle,D., Schach,U., Fabian,C. and Nusslein-Volhard,C. (1996) The identification of genes with unique and essential functions in the development of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Development, 123, 1–36. - PubMed
-
- Anderson K.V. (2000) Finding the genes that direct mammalian development: ENU mutagenesis in the mouse. Trends Genet., 16, 99–102. - PubMed
-
- Zambrowicz B.P., Friedrich,G.A., Buxton,E.C., Lilleberg,S.L., Person,C. and Sands,A.T. (1998) Disruption and sequence identification of 2,000 genes in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature, 392, 608–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

