Hairpin-duplex equilibrium reflected in the A-->B transition in an undecamer quasi-palindrome present in the locus control region of the human beta-globin gene cluster
- PMID: 14627823
- PMCID: PMC290256
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg887
Hairpin-duplex equilibrium reflected in the A-->B transition in an undecamer quasi-palindrome present in the locus control region of the human beta-globin gene cluster
Abstract
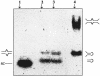
Our recent work on an A-->G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) at the quasi-palindromic sequence d(TGGGG[A/G]CCCCA) of HS4 of the human beta-globin locus control region in an Indian population showed a significant association between the G allele and the occurrence of beta-thalassemia. Using UV-thermal denaturation, gel assay, circular dichroism (CD) and nuclease digestion experiments we have demonstrated that the undecamer quasi- palindromic sequence d(TGGGGACCCCA) (HPA11) and its reported polymorphic (SNP) version d(TGG GGGCCCCA) (HPG11) exist in hairpin-duplex equilibria. The biphasic nature of the melting profiles for both the oligonucleotides persisted at low as well as high salt concentrations. The HPG11 hairpin showed a higher T(m) than HPA11. The presence of unimolecular and bimolecular species was also shown by non-denaturating gel electrophoresis experiments. The CD spectra of both oligonucleotides showed features of the A- as well as B-type conformations and, moreover, exhibited a concentration dependence. The disappearance of the 265 nm positive CD signal in an oligomer concentration-dependent manner is indicative of an A-->B transition. The results give unprecedented insight into the in vitro structure of the quasi-palindromic sequence and provide the first report in which a hairpin-duplex equilibrium has been correlated with an A-->B interconversion of DNA. The nuclease-dependent degradation suggests that HPG11 is more resistant to nuclease than HPA11. Multiple sequence alignment of the HS4 region of the beta-globin gene cluster from different organisms revealed that this quasi-palindromic stretch is unique to Homo sapiens. We propose that quasi-palindromic sequences may form stable mini- hairpins or cruciforms in the HS4 region and might play a role in regulating beta-globin gene expression by affecting the binding of transcription factors.
Figures











References
-
- Sinden R.R. (1994) DNA Structure and Function. Academic Press, New York, NY.
-
- Saenger W. (1984) Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure. Springer-Verlag, New York, NY.
-
- Brahmachari S.K., Meera,G., Sarkar,P.S., Balagurumoorthy,P., Tripathi,J., Raghavan,S., Shaligram,U. and Pataskar,S. (1995) Simple repetitive sequences in the genome: structure and functional significance. Electrophoresis, 16, 1705–1714. - PubMed
-
- Kim J.L., Nikolov,D.B. and Burley,S.K. (1993) Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of TATA element. Nature, 365, 520–527. - PubMed

