Regulation of the human GLUT4 gene promoter: interaction between a transcriptional activator and myocyte enhancer factor 2A
- PMID: 14630949
- PMCID: PMC299781
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2432756100
Regulation of the human GLUT4 gene promoter: interaction between a transcriptional activator and myocyte enhancer factor 2A
Abstract
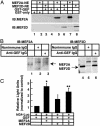
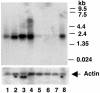
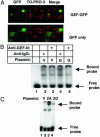
The GLUT4 gene is subject to complex tissue-specific and metabolic regulation, with a profound impact on insulin-mediated glucose disposal. We have shown, by using transgenic mice, that the human GLUT4 promoter is regulated through the cooperative function of two distinct regulatory elements, domain 1 and the myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) domain. The MEF2 domain binds transcription factors MEF2A and MEF2D in vivo. Domain I binds a transcription factor, GLUT4 enhancer factor (GEF). In this report, we show a restricted pattern of GEF expression in human tissues, which overlaps with MEF2A only in tissues expressing high levels of GLUT4, suggesting the hypothesis that GEF and MEF2A function together to activate GLUT4 transcription. Data obtained from transiently transfected cells support this hypothesis. Neither GEF nor MEF2A alone significantly activated GLUT4 promoter activity, but increased promoter activity 4- to 5-fold when expressed together. Deletion of the GEF-binding domain (domain I) and the MEF2-binding domain prevented activation, strengthening the conclusion that promoter regulation occurs through these elements. GEF and MEF2A, isolated from nuclei of transfected cells, bound domain I and the MEF2 domain, respectively, which is consistent with activation through these regulatory elements. Finally, GEF and MEF2A coimmunoprecipitated in vivo, strongly supporting a mechanism of GLUT4 transcription activation that depends on this protein-protein interaction.
Figures



Similar articles
-
GLUT4 enhancer factor (GEF) interacts with MEF2A and HDAC5 to regulate the GLUT4 promoter in adipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 21;283(12):7429-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800481200. Epub 2008 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18216015 Free PMC article.
-
Myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2)-binding site is required for GLUT4 gene expression in transgenic mice. Regulation of MEF2 DNA binding activity in insulin-deficient diabetes.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 5;273(23):14285-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.23.14285. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9603935
-
Regulation of muscle GLUT4 enhancer factor and myocyte enhancer factor 2 by AMP-activated protein kinase.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Dec;289(6):E1071-6. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00606.2004. Epub 2005 Aug 16. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005. PMID: 16105857
-
Mechanisms regulating GLUT4 glucose transporter expression and glucose transport in skeletal muscle.Acta Physiol Scand. 2005 Jan;183(1):43-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201X.2004.01380.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2005. PMID: 15654919 Review.
-
The Molecular and Biological Function of MEF2D in Leukemia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1459:379-403. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-62731-6_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39017853 Review.
Cited by
-
Zinc finger protein 407 (ZFP407) regulates insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and glucose transporter 4 (Glut4) mRNA.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 6;290(10):6376-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.623736. Epub 2015 Jan 16. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25596527 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cardiomyocyte Glut4 expression by ZAC1.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 28;285(22):16942-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.097246. Epub 2010 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20363751 Free PMC article.
-
The PGC-1α-related coactivator promotes mitochondrial and myogenic adaptations in C2C12 myotubes.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Oct;301(4):R864-72. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00232.2011. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21795630 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple signalling pathways redundantly control glucose transporter GLUT4 gene transcription in skeletal muscle.J Physiol. 2009 Sep 1;587(Pt 17):4319-27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.174888. Epub 2009 Jul 13. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19596898 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of SIK1 by phanginin A regulates skeletal muscle glucose uptake by phosphorylating HADC4/5/7 and enhancing GLUT4 expression and translocation.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2025 Apr 7;15(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s13659-025-00504-z. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2025. PMID: 40192973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsao, T. S., Burcelin, R., Katz, E. B., Huang, L. & Charron, M. J. (1996) Diabetes 45, 28–36. - PubMed
-
- Treadway, J. L., Hargrove, D. M., Nardone, N. A., McPherson, R. K., Russo, J. F., Milici, A. J., Stukenbrok, H. A., Gibbs, E. M., Stevenson, R. W. & Pessin, J. E. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269, 29956–29961. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd, P. R., Gnudi, L., Tozzo, E., Yang, H., Leach, F. & Kahn, B. B. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268, 22243–22246. - PubMed
-
- Leturque, A., Loizeau, M., Vaulont, S., Salminen, M. & Girard, J. (1996) Diabetes 45, 23–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

