Passive transfer of flt-3L-derived dendritic cells delays diabetes development in NOD mice and associates with early production of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-10 in the spleen of recipient mice
- PMID: 14632742
- PMCID: PMC1808900
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2003.02308.x
Passive transfer of flt-3L-derived dendritic cells delays diabetes development in NOD mice and associates with early production of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-10 in the spleen of recipient mice
Abstract
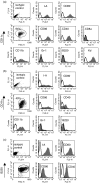
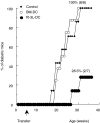
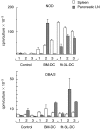
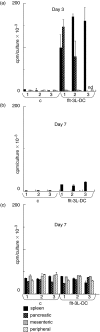
CD11c+/CD11b+dendritic cells (DC) with high levels of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II and co-stimulatory molecules have been derived from spleen cells cultured with granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) + flt-3L + interleukin (IL)-6 (flt-3L-DC). Investigating in vivo the function of DC in non-obese diabetic mice (NOD), we showed that a single injection of this in vitro-derived subset of DC prevents the development of diabetes into prediabetic female mice. In contrast, DC derived from bone marrow cells cultured with GM-CSF + IL-4 [bone marrow (BM)-DC] induced no protection. Moreover, protection against diabetes following injection of flt-3L-DC was associated with IL-4 and IL-10 production in the spleen and the pancreatic lymph nodes of recipient mice, indicating that this DC population is able to polarize the immune response towards a Th2 pathway. As we shown previously, NOD BM-DC exhibit an enhanced capacity to produce IL-12p70 in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and anti-CD40 stimulation compared to BM-DC from control mice. In contrast, NOD flt-3L-DC, as their control mouse counterpart, produced no IL-12p70 to these stimuli. Our findings show that a subset of DC, characterized by a mature phenotype and the absence of IL-12p70 production can be derived from NOD mouse spleen favouring IL-4 and IL-10 regulatory responses and protection from diabetes development.
Figures
References
-
- Lederman MM, Ellner JJ, Rodman HM. Defective suppressor cell generation in juvenile onset diabetes. J Immunol. 1981;127:2051–5. - PubMed
-
- Topliss D, How J, Lewis M, Row V, Volpe R. Evidence for cell-mediated immunity and specific suppressor T lymphocyte dysfunction in Graves’ disease and diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983;57:700–5. - PubMed
-
- Lohmann D, Krug J, Lampeter EF, Bierwolf B, Verlohren HJ. Cell-mediated immune reactions against B cells and defect of suppressor cell activity in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1986;29:421–5. - PubMed
-
- Serreze DV, Leiter EH. Defective activation of T suppressor cell function in nonobese diabetic mice. Potential relation to cytokine deficiencies. J Immunol. 1988;140:3801–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

