Dopamine acutely decreases apical membrane Na/H exchanger NHE3 protein in mouse renal proximal tubule
- PMID: 14633135
- PMCID: PMC4114392
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00308.x
Dopamine acutely decreases apical membrane Na/H exchanger NHE3 protein in mouse renal proximal tubule
Abstract
Background: Dopamine is a principal natriuretic hormone in mammalian Na+ homeostasis. Dopamine acutely alters glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and decreases Na+ absorption in both the proximal and distal nephron. Proximal tubule natriuresis is effected through inhibition of the apical membrane Na/H exchanger NHE3.
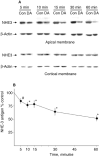
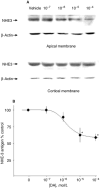
Methods: We examined whether dopamine directly and acutely decreases apical membrane NHE3 protein using renal tissue in two in vitro systems: renal cortical slices and in vitro perfused single tubules. After incubation with dopamine, NHE3 activity was measured by 22Na flux and NHE3 antigen was measured by immunoblot in apical membrane and total cellular membranes.
Results: Direct application of dopamine to either cortical slices or microperfused tubules acutely decreases NHE3 activity and antigen at the apical membrane of the proximal tubule. No change in total cellular NHE3 was detected.
Conclusion: One mechanism by which dopamine causes natriuresis is via direct and acute reduction of NHE3 protein at the apical membrane via changes in NHE3 protein trafficking.
Figures




References
-
- Hollenberg NK, Adams DF, Mendell P, et al. Renal vascular responses to dopamine: Hemodynamic and angiographic observations in normal man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973;45:733–742. - PubMed
-
- Bello-Reuss E, Pastoraiza-Munoz E, Colindres RE. Dopamine decreases fluid reabsorption in straight portions of rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1977;232:F26–F32. - PubMed
-
- Grider J, Kilpatrick E, Ott C, Jackson B. Effect of dopamine on NaCl transport in the medullary thick ascending limb of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;342:281–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

