Infiltration of neutrophils is required for acquisition of metastatic phenotype of benign murine fibrosarcoma cells: implication of inflammation-associated carcinogenesis and tumor progression
- PMID: 14633597
- PMCID: PMC1892401
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63580-8
Infiltration of neutrophils is required for acquisition of metastatic phenotype of benign murine fibrosarcoma cells: implication of inflammation-associated carcinogenesis and tumor progression
Abstract
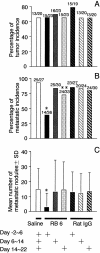
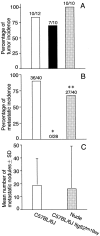
QR-32 tumor cells, a clone derived from a murine fibrosarcoma, are poorly tumorigenic and nonmetastatic when injected into syngeneic C57BL/6 mice. However, they are converted to highly malignant ones once they have grown in vivo after being co-implanted in a subcutaneous site with a foreign body, a gelatin sponge. Early phase of inflammation induced by the gelatin sponge participates in the conversion and histological analysis shows predominant infiltration of neutrophils. The objective of this study was to determine whether the depletion of the infiltrating neutrophils has any effect on the tumor progression. Intraperitoneal administration of a monoclonal anti-granulocyte antibody, RB6-8C5 (RB6), depleted neutrophils from both the peripheral blood circulation and the local inflamed site in mice with co-implantation of QR-32 tumor cells and gelatin sponge. The RB6 administration did not inhibit either tumor development or growth of QR-32 tumor cells. In contrast, tumor cell lines established from RB6-administered mice showed a significant decrease in metastatic incidence as compared with the tumor cell lines obtained from the mice with administration of control rat IgG or saline. Metastatic ability was significantly suppressed when RB6 had been administered in the early phase (from day -2 to day 6 after implantation); however, the administration in the middle (from day 6 to day 14) or late (from day 14 to day 22) phase did not affect the metastatic ability. We confirmed the phenomena by using integrin beta(2) knockout mice that had impaired neutrophil infiltration into inflamed sites. In the knockout mice, neutrophils hardly infiltrated into the gelatin sponge and the tumors showed dramatically suppressed metastatic phenotype as compared with those in wild-type mice or nude mice. Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated that expressions of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine and nitrotyrosine were parallel to those in the presence of neutrophils. These results suggested that inflammation, especially when neutrophils infiltrate into tumor tissue, is primarily important for benign tumor cells to acquire metastatic phenotype.
Figures



References
-
- Ohshima H, Bartsch H: Chronic infections and inflammatory processes as cancer risk factors: possible role of nitric oxide in carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 1994, 305:253-264 - PubMed
-
- Levin B: Ulcerative colitis and colon cancer: biology and surveillance. J Cell Biochem Suppl 1992, 16G:47-50 - PubMed
-
- Tiollais P, Pourcel C, Dejean A: The hepatitis B virus. Nature 1985, 317:489-495 - PubMed
-
- Rosin MP, Anwar WA, Ward AJ: Inflammation, chromosomal instability, and cancer: the schistosomiasis model. Cancer Res 1994, 54:1929s-1933s - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

