Septic mice are susceptible to pulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 14633632
- PMCID: PMC1892404
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63615-2
Septic mice are susceptible to pulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
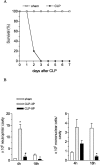
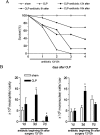
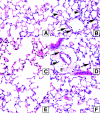
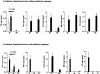
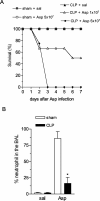
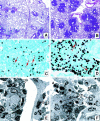
Clinical data underscores the fact that subsequent high mortality rates occur in patients who survive acute septic episodes. Herein, we described a clinically relevant model of experimental sepsis that we believe will allow further investigation of the manner in which the pulmonary innate immune response is modulated after sepsis. C57BL/6 mice were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) model, whereby the cecum was partially ligated and punctured nine times with a 21-gauge needle. This procedure was associated with 100% mortality at 3 days after surgery. In contrast, when mice subjected to CLP were treated with antibiotic beginning at 8 hours after surgery, and every 12 hours thereafter until 3 days, approximately 60% of the mice survived. Interestingly, CLP survivors quickly succumbed (100% mortality) to pulmonary infection when intratracheally challenged, at day 3 after CLP, with viable Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. No mortality was observed in conidia-challenged sham-operated mice. The defective innate immune response against A. fumigatus in CLP mice could not be explained by a failure of neutrophils to infiltrate the lungs. Instead, gene array analysis revealed that several components of the innate immune response, including the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway, were down-regulated. Thus, we describe a system of sepsis-induced innate immune failure in the lungs of C57BL/6 mice.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immunomodulatory role of CXCR2 during experimental septic peritonitis.J Immunol. 2003 Oct 1;171(7):3775-84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.7.3775. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14500678
-
Interleukin-12 and -18 induce severe liver injury in mice recovered from peritonitis after sublethal endotoxin challenge.Surgery. 2003 Jul;134(1):92-100. doi: 10.1067/msy.2003.189. Surgery. 2003. PMID: 12874588
-
CXC chemokine receptor-2 ligands are necessary components of neutrophil-mediated host defense in invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.J Immunol. 1999 Dec 1;163(11):6086-94. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10570298
-
Role of TNF-alpha in pulmonary host defense in murine invasive aspergillosis.J Immunol. 1999 Feb 1;162(3):1633-40. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 9973423
-
Innate immune response to peritoneal bacterial infection.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2022;371:43-61. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2022.04.014. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35965000 Review.
Cited by
-
A multivariable prediction model for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients with acute respiratory failure (IPA-GRRR-OH score).Intensive Care Med. 2025 Jan;51(1):72-81. doi: 10.1007/s00134-024-07767-z. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Intensive Care Med. 2025. PMID: 39853358
-
Activation of Hepatic STAT3 Maintains Pulmonary Defense during Endotoxemia.Infect Immun. 2015 Oct;83(10):4015-27. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00464-15. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26216424 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptors in immunity and inflammatory diseases: Past, present, and future.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Jun;59:391-412. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 May 4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29730580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD1d- and MR1-Restricted T Cells in Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2015 Aug 12;6:401. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00401. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26322041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and cellular aspects of sepsis-induced immunosuppression.J Mol Med (Berl). 2008 May;86(5):495-506. doi: 10.1007/s00109-007-0300-4. Epub 2008 Feb 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18259721 Review.
References
-
- Perl TM, Dvorak L, Hwang T, Wenzel RP: Long-term survival and function after suspected Gram-negative sepsis. JAMA 1995, 274:338-345 - PubMed
-
- Bone RC: Gram-negative sepsis. Background, clinical features, and intervention. Chest 1991, 100:802-808 - PubMed
-
- Martin MA: Epidemiology and clinical impact of gram-negative sepsis. Infect Dis Clin North Am 1991, 5:739-752 - PubMed
-
- Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW, Swanson PE, Grayson MH, Osborne DF, Wagner TH, Cobb JP, Coopersmith C, Karl IE: Depletion of dendritic cells, but not macrophages, in patients with sepsis. J Immunol 2002, 168:2493-2500 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

