Septic mice are susceptible to pulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 14633632
- PMCID: PMC1892404
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63615-2
Septic mice are susceptible to pulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
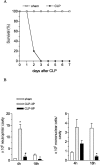
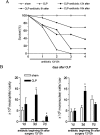
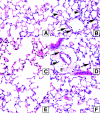
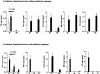
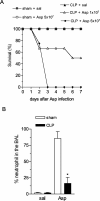
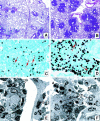
Clinical data underscores the fact that subsequent high mortality rates occur in patients who survive acute septic episodes. Herein, we described a clinically relevant model of experimental sepsis that we believe will allow further investigation of the manner in which the pulmonary innate immune response is modulated after sepsis. C57BL/6 mice were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) model, whereby the cecum was partially ligated and punctured nine times with a 21-gauge needle. This procedure was associated with 100% mortality at 3 days after surgery. In contrast, when mice subjected to CLP were treated with antibiotic beginning at 8 hours after surgery, and every 12 hours thereafter until 3 days, approximately 60% of the mice survived. Interestingly, CLP survivors quickly succumbed (100% mortality) to pulmonary infection when intratracheally challenged, at day 3 after CLP, with viable Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. No mortality was observed in conidia-challenged sham-operated mice. The defective innate immune response against A. fumigatus in CLP mice could not be explained by a failure of neutrophils to infiltrate the lungs. Instead, gene array analysis revealed that several components of the innate immune response, including the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway, were down-regulated. Thus, we describe a system of sepsis-induced innate immune failure in the lungs of C57BL/6 mice.
Figures


References
-
- Perl TM, Dvorak L, Hwang T, Wenzel RP: Long-term survival and function after suspected Gram-negative sepsis. JAMA 1995, 274:338-345 - PubMed
-
- Bone RC: Gram-negative sepsis. Background, clinical features, and intervention. Chest 1991, 100:802-808 - PubMed
-
- Martin MA: Epidemiology and clinical impact of gram-negative sepsis. Infect Dis Clin North Am 1991, 5:739-752 - PubMed
-
- Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW, Swanson PE, Grayson MH, Osborne DF, Wagner TH, Cobb JP, Coopersmith C, Karl IE: Depletion of dendritic cells, but not macrophages, in patients with sepsis. J Immunol 2002, 168:2493-2500 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

