The phosphorylation state of an autoregulatory domain controls PACS-1-directed protein traffic
- PMID: 14633983
- PMCID: PMC291837
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg596
The phosphorylation state of an autoregulatory domain controls PACS-1-directed protein traffic
Abstract
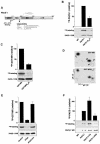
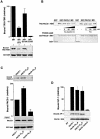
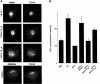
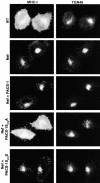
PACS-1 is a cytosolic sorting protein that directs the localization of membrane proteins in the trans-Golgi network (TGN)/endosomal system. PACS-1 connects the clathrin adaptor AP-1 to acidic cluster sorting motifs contained in the cytoplasmic domain of cargo proteins such as furin, the cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor and in viral proteins such as human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef. Here we show that an acidic cluster on PACS-1, which is highly similar to acidic cluster sorting motifs on cargo molecules, acts as an autoregulatory domain that controls PACS-1-directed sorting. Biochemical studies show that Ser278 adjacent to the acidic cluster is phosphorylated by CK2 and dephosphorylated by PP2A. Phosphorylation of Ser278 by CK2 or a Ser278-->Asp mutation increased the interaction between PACS-1 and cargo, whereas a Ser278-->Ala substitution decreased this interaction. Moreover, the Ser278-->Ala mutation yields a dominant-negative PACS-1 molecule that selectively blocks retrieval of PACS-1-regulated cargo molecules to the TGN. These results suggest that coordinated signaling events regulate transport within the TGN/endosomal system through the phosphorylation state of both cargo and the sorting machinery.
Figures

References
-
- Blagoveshchenskaya A.D., Thomas,L., Feliciangeli,S.F., Hung,C.H. and Thomas,G. (2002) HIV-1 Nef downregulates MHC-I by a PACS-1- and PI3K-regulated ARF6 endocytic pathway. Cell, 111, 853–866. - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino J.S. and Traub,L.M. (2003) Signals for sorting of transmembrane proteins to endosomes and lysosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 72, 395–447. - PubMed
-
- Chen H.J., Yuan,J. and Lobel,P. (1997) Systematic mutational analysis of the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor cytoplasmic domain. An acidic cluster containing a key aspartate is important for function in lysosomal enzyme sorting. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 7003–7012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

