E2F7, a novel E2F featuring DP-independent repression of a subset of E2F-regulated genes
- PMID: 14633988
- PMCID: PMC291854
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg613
E2F7, a novel E2F featuring DP-independent repression of a subset of E2F-regulated genes
Abstract
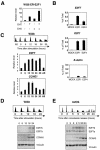
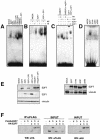
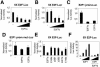
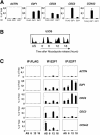
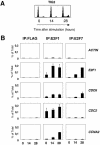
The E2F family of transcription factors play an essential role in the regulation of cell cycle progression. In a screen for E2F-regulated genes we identified a novel E2F family member, E2F7. Like the recently identified E2F-like proteins of Arabidopsis, E2F7 has two DNA binding domains and binds to the E2F DNA binding consensus site independently of DP co-factors. Consistent with being an E2F target gene, we found that the expression of E2F7 is cell cycle regulated. Ectopic expression of E2F7 results in suppression of E2F target genes and accumulation of cells in G1. Furthermore, E2F7 associates with E2F-regulated promoters in vivo, and this association increases in S phase. Interestingly, however, E2F7 binds only a subset of E2F-dependent promoters in vivo, and in agreement with this, inhibition of E2F7 expression results in specific derepression of these promoters. Taken together, these data demonstrate that E2F7 is a unique repressor of a subset of E2F target genes whose products are required for cell cycle progression.
Figures


References
-
- Cartwright P., Muller,H., Wagener,C., Holm,K. and Helin,K. (1998) E2F-6: a novel member of the E2F family is an inhibitor of E2F-dependent transcription. Oncogene, 17, 611–623. - PubMed
-
- Courjal F., Louason,G., Speiser,P., Katsaros,D., Zeillinger,R. and Theillet,C. (1996) Cyclin gene amplification and overexpression in breast and ovarian cancers: evidence for the selection of cyclin D1 in breast and cyclin E in ovarian tumors. Int. J. Cancer, 69, 247–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

