Immunohistochemical determination of HER-2/neu, c-Kit (CD117), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) overexpression in malignant melanoma
- PMID: 14634801
- PMCID: PMC12161809
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-003-0509-8
Immunohistochemical determination of HER-2/neu, c-Kit (CD117), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) overexpression in malignant melanoma
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the prevalence and evaluate the possible prognostic value of the molecular targets in malignant melanoma, we studied the overexpression of HER-2/neu, c-Kit, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in this patient population.
Materials and methods: Overexpression of HER-2/neu, c-Kit, and VEGF was evaluated using immunohistochemical assays in 202 archival tissue specimens.
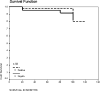
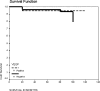
Results: Only two patients (0.9%) revealed HER-2/neu overexpression, whereas 46 (22.8%) revealed c-Kit and 42 (20.8%) specimens showed VEGF overexpression. Multivariate analysis performed did not show a significant difference in survival between c-Kit-positive and c-Kit-negative groups (P = 0.36) and VEGF-positive and VEGF-negative groups (P = 0.25). Interestingly, c-Kit was more likely to be overexpressed in the superficial spreading type and VEGF was overexpressed preferentially in the amelanotic melanoma type.
Conclusions: HER-2/neu has no role in melanogenesis. Both c-Kit (expressed in superficial spreading disease) and VEGF (expressed in amelanotic melanoma) may have significant therapeutic implications as molecular targets, which warrants further investigation.
Figures
References
-
- Kopf AW, Salopek TG, Slade J, et al (1995) Techniques of cutaneous examination for the detection of skin cancer. Cancer 75:684–690 - PubMed
-
- Ullrich A, Schlessinger J (1990) Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 61:203–212 - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, et al (1989) Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 244:707–712 - PubMed
-
- Yu D, Wang SS, Dulski KM, et al (1994) c-erbB-2/neu overexpression enhances metastatic potential of human lung cancer cells by induction of metastasis-associated properties. Cancer Res 54:3260–3266 - PubMed
-
- Tsugawa K, Fushida S, Yonemura Y (1993) Amplification of the c-erbB-2 gene in gastric carcinoma: correlation with survival. Oncology 50:418–425 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous