Synergism of gamma interferon and interleukin-5 in the control of murine filariasis
- PMID: 14638787
- PMCID: PMC308906
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.12.6978-6985.2003
Synergism of gamma interferon and interleukin-5 in the control of murine filariasis
Abstract
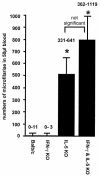
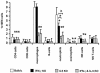
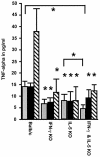
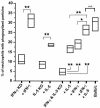
There has been a prevailing perception that Th1 and Th2 immune responses induce antagonistic immune effector mechanisms during an infection. We investigated the role of the Th1 cytokine gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and the Th2 cytokine interleukin-5 (IL-5) in murine filariasis infections with the rodent filarial nematode Litomosoides sigmodontis with regard to immune responses to the parasite. Earlier data showed an important role for IL-5 and IFN-gamma in effective immune responses to filarial infection. Therefore, in this study it was asked whether IL-5 and IFN-gamma act synergistically or antagonistically. Indeed, IL-5 as well as IFN-gamma knockout (KO) mice show a higher worm load than the wild-type controls. IFN-gamma/IL-5 double-KO mice had a significantly higher worm load than any of the single-KO mice, suggesting a synergism between IFN-gamma and IL-5 in controlling worm infection. Neutrophils are known to play an important role for the containment and encapsulation process of the worms. In infected IFN-gamma KO, IL-5 KO, and IFN-gamma/IL-5 double-KO mice, neutrophils were significantly reduced in chemotactic activity levels compared to controls. In addition, the level of phagocytosis activity of neutrophils from IFN-gamma/IL-5 double-KO mice was further decreased in comparison to that of the single-KO mice. Levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha, which is an important factor for neutrophil activation, were found to be reduced in macrophages from KO mice. In conclusion, these results argue for immune effector mechanisms in murine filarial infection that are dependent on both IFN-gamma and IL-5. Synergistic effects of the two cytokines may be mediated, at least in part, by neutrophils for the control of adult worms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of interferon-gamma confers impaired neutrophil granulocyte function and imparts prolonged survival of adult filarial worms in murine filariasis.Microbes Infect. 2001 Mar;3(3):203-13. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01372-7. Microbes Infect. 2001. PMID: 11358714
-
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) counterregulates IL-4-dependent effector mechanisms in Murine Filariasis.Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6287-93. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6287-6293.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501755 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of IL-17A in Litomosoides sigmodontis-infected mice influences worm development and drives elevated filarial-specific IFN-γ.Parasitol Res. 2018 Aug;117(8):2665-2675. doi: 10.1007/s00436-018-5959-7. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Parasitol Res. 2018. PMID: 29931394 Free PMC article.
-
The immune response of inbred laboratory mice to Litomosoides sigmodontis: A route to discovery in myeloid cell biology.Parasite Immunol. 2020 Jul;42(7):e12708. doi: 10.1111/pim.12708. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Parasite Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32145033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophils: Friend or foe in Filariasis?Parasite Immunol. 2022 Jun;44(6):e12918. doi: 10.1111/pim.12918. Epub 2022 May 25. Parasite Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35373850 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of eosinophils and neutrophils in innate and adaptive protective immunity to larval strongyloides stercoralis in mice.Infect Immun. 2006 Oct;74(10):5730-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01958-05. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16988250 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization with Brugia malayi Myosin as Heterologous DNA Prime Protein Boost Induces Protective Immunity against B. malayi Infection in Mastomys coucha.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 9;11(11):e0164991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164991. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27828973 Free PMC article.
-
Similarity and diversity in macrophage activation by nematodes, trematodes, and cestodes.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:262609. doi: 10.1155/2010/262609. Epub 2010 Jan 26. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20145705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Filarial parasites develop faster and reproduce earlier in response to host immune effectors that determine filarial life expectancy.PLoS Biol. 2010 Oct 19;8(10):e1000525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000525. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 20976099 Free PMC article.
-
Fat-associated lymphoid clusters control local IgM secretion during pleural infection and lung inflammation.Nat Commun. 2016 Sep 1;7:12651. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12651. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27582256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, J., A. R. Satoskar, and D. G. Russell. 1999. Leishmania species: models of intracellular parasitism. J. Cell Sci. 112:2993-3002. - PubMed
-
- Al-Qaoud, K. M., B. Fleischer, and A. Hoerauf. 1998. The Xid defect imparts susceptibility to experimental murine filariosis—association with a lack of antibody and IL-10 production by B cells in response to phosphorylcholine. Int. Immunol. 10:17-25. - PubMed
-
- Al-Qaoud, K. M., E. Pearlman, J. Klukowski, T. Hartung, B. Fleischer, and A. Hoerauf. 2000. A new mechanism for IL-5-dependent helminth control: neutrophil accumulation and neutrophil-mediated worm encapsulation in murine filariasis are abolished in the absence of IL-5. Int. Immunol. 12:899-908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

