Deletion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis sigma factor E results in delayed time to death with bacterial persistence in the lungs of aerosol-infected mice
- PMID: 14638810
- PMCID: PMC308924
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.12.7170-7172.2003
Deletion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis sigma factor E results in delayed time to death with bacterial persistence in the lungs of aerosol-infected mice
Abstract
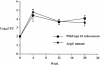
The stress-induced extracytoplasmic sigma factor E (SigE) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis shows increased expression after heat shock, sodium dodecyl sulfate treatment, and oxidative stress, as well as after phagocytosis in macrophages. We report that deletion of sigE results in delayed lethality in mice without a significant reduction of bacterial numbers in lungs.
Figures

References
-
- Brandt, L., J. Feino Cunha, A. W. Olsen, B. Chilima, P. Hirsch, R. Appelberg, and P. Andersen. 2002. Failure of the Mycobacterium bovis BCG vaccine: some species of environmental mycobacteria block multiplication of BCG and induction of protective immunity to tuberculosis. Infect. Immun. 70:672-678. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cole, S. T., R. Brosch, J. Parkhill, T. Garnier, C. Churcher, D. Harris, S. V. Gordon, K. Eiglmeier, S. Gas, C. E. Barry III, F. Tekaia, K. Badcock, D. Basham, D. Brown, T. Chillingworth, R. Connor, R. Davies, K. Devlin, T. Feltwell, S. Gentles, N. Hamlin, S. Holroyd, T. Hornsby, K. Jagels, and B. G. Barrell. 1998. Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. Nature 393:537-544. - PubMed
-
- Davis, N. K., and K. F. Chater. 1992. The Streptomyces coelicolor whiB gene encodes a small transcription factor-like protein dispensable for growth but essential for sporulation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 232:351-358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

