Nucleolin expressed at the cell surface is a marker of endothelial cells in angiogenic blood vessels
- PMID: 14638862
- PMCID: PMC2173679
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200304132
Nucleolin expressed at the cell surface is a marker of endothelial cells in angiogenic blood vessels
Abstract
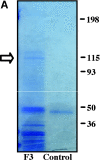
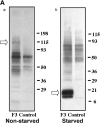
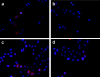
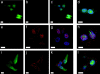
A tumor-homing peptide, F3, selectively binds to endothelial cells in tumor blood vessels and to tumor cells. Here, we show that the cell surface molecule recognized by F3 is nucleolin. Nucleolin specifically bound to an F3 peptide affinity matrix from extracts of cultured breast carcinoma cells. Antibodies and cell surface biotin labeling revealed nucleolin at the surface of actively growing cells, and these cells bound and internalized fluorescein-conjugated F3 peptide, transporting it into the nucleus. In contrast, nucleolin was exclusively nuclear in serum-starved cells, and F3 did not bind to these cells. The binding and subsequent internalization of F3 were blocked by an antinucleolin antibody. Like the F3 peptide, intravenously injected antinucleolin antibodies selectively accumulated in tumor vessels and in angiogenic vessels of implanted "matrigel" plugs. These results show that cell surface nucleolin is a specific marker of angiogenic endothelial cells within the vasculature. It may be a useful target molecule for diagnostic tests and drug delivery applications.
Figures


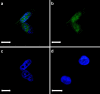
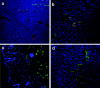
References
-
- Arap, W., R. Pasqualini, and E. Ruoslahti. 1998. Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science. 279:377–380. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet, H., O. Filhol, I. Truchet, P. Brethenou, C. Cochet, F. Amalric, and G. Bouche. 1996. Fibroblast growth factor-2 binds to the regulatory beta subunit of CK2 and directly stimulates CK2 activity toward nucleolin. J. Biol. Chem. 271:24781–24787. - PubMed
-
- Borer, R.A., C.F. Lehner, H.M. Eppenberger, and E.A. Nigg. 1989. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 56:379–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

