Detection of human herpesvirus-6 in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy surgical brain resections
- PMID: 14638964
- PMCID: PMC4294224
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000094357.10782.f9
Detection of human herpesvirus-6 in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy surgical brain resections
Abstract
Background: Human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6), a ubiquitous beta-herpesvirus, is the causative agent of roseola infantum and has been associated with a number of neurologic disorders including seizures, encephalitis/meningitis, and multiple sclerosis. Although the role of HHV-6 in human CNS disease remains to be fully defined, a number of studies have suggested that the CNS can be a site for persistent HHV-6 infection.
Objective: To characterize the extent and distribution of HHV-6 in human glial cells from surgical brain resections of patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE).
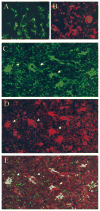
Method: Brain samples from eight patients with MTLE and seven patients with neocortical epilepsy (NE) undergoing surgical resection were quantitatively analyzed for the presence of HHV-6 DNA using a virus-specific real-time PCR assay. HHV-6 expression was also characterized by western blot analysis and in situ immunohistochemistry (IHC). In addition, HHV-6-reactive cells were analyzed for expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) by double immunofluorescence.
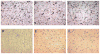
Results: DNA obtained from four of eight patients with MTLE had significantly elevated levels of HHV-6 as quantified by real-time PCR. HHV-6 was not amplified in any of the seven patients with NE undergoing surgery. The highest levels of HHV-6 were demonstrated in hippocampal sections (up to 23,079 copies/10(6) cells) and subtyped as HHV-6B. Expression of HHV-6 was confirmed by western blot analysis and IHC. HHV-6 was co-localized to GFAP-positive cells that morphologically appeared to be astrocytes.
Conclusions: HHV-6B is present in brain specimens from a subset of patients with MTLE and localized to astrocytes in the absence of inflammation. The amplification of HHV-6 from hippocampal and temporal lobe astrocytes of MTLE warrants further investigation into the possible role of HHV-6 in the development of MTLE.
Figures
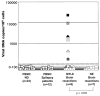

 = Patient 3; ▨
= Patient 3; ▨
 = Patient 6;
= Patient 6;

 = Patient 15.
= Patient 15.
References
-
- Salahuddin SZ, Ablashi DV, Markham PD, et al. Isolation of a new virus, HBLV, in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders. Science. 1986;234:596–601. - PubMed
-
- Caserta MT, Mock DJ, Dewhurst S. Human herpesvirus 6. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:829–833. - PubMed
-
- Albright AV, Lavi E, Black JB, Goldberg S, O’Connor MJ, Gonzalez–Scarano F. The effect of human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) on cultured human neural cells: oligodendrocytes and microglia. J Neurovirol. 1998;4:486–494. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
