The impact of splice isoforms on voltage-gated calcium channel alpha1 subunits
- PMID: 14645450
- PMCID: PMC1664792
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.052712
The impact of splice isoforms on voltage-gated calcium channel alpha1 subunits
Abstract
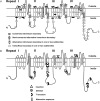
Semi-conserved exon boundaries in members of the CACNA1 gene family result in recurring pre-mRNA splicing patterns. The resulting variations in the encoded pore-forming subunit of the voltage-gated calcium channel affect functionally significant regions, such as the vicinity of the voltage-sensing S4 segments or the intracellular loops that are important for protein interaction. In addition to generating functional diversity, RNA splicing regulates the quantitative expression of other splice isoforms of the same gene by producing transcripts with premature stop codons which encode two-domain or three-domain channels. An overview of some of the known splice isoforms of the alpha(1) calcium channel subunits and their significance is given.
Figures
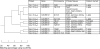
References
-
- Abernethy DR, Soldatov NM. Structure-functional diversity of human l-type Ca2+ channel: perspectives for new pharmacological targets. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;300:724–728. - PubMed
-
- Anderson PA, Greenberg RM. Phylogeny of ion channels: clues to structure and function. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2001;129:17–28. - PubMed
-
- Beam KG, Adams BA, Niidome T, Numa S, Tanabe T. Function of a truncated dihydropyridine receptor as both voltage sensor and calcium channel. Nature. 1992;360:169–171. - PubMed
-
- Berke JD, Sgambato V, Zhu PP, Lavoie B, Vincent M, Krause M, Hyman SE. Dopamine and glutamate induce distinct striatal splice forms of Ania-6, an RNA polymerase II-associated cyclin. Neuron. 2001;32:277–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

