The sleep-modulating peptide cortistatin augments the h-current in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 14645483
- PMCID: PMC6740974
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-34-10884.2003
The sleep-modulating peptide cortistatin augments the h-current in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
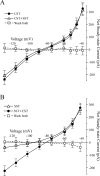
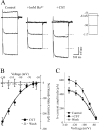
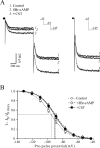
Cortistatin (CST) is a sleep-modulating peptide found exclusively in the brain. Although CST is closely related to somatostatin (SST) and binds to SST receptors, CST has effects on sleep and neuronal activity in cortex and hippocampus that differ from SST. To uncover the cellular mechanisms affected by CST, we studied the electrophysiological postsynaptic effects of CST and assessed its interaction with SST on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. CST altered intrinsic membrane properties and occluded SST effects, indicating that both peptides similarly augment the sustained K+ M- and leak-currents (IM and IK(L)). In the presence of SST, however, CST elicited an additional inwardly rectifying component in the hyperpolarized range. This effect was unaffected by barium, used to block K+ currents, but was completely prevented by the selective h-current (Ih) blocker ZD7288. CST, but not SST, selectively increased Ih in a concentration-dependent manner by augmenting its maximum conductance. CST did not shift the Ih activation curve, and the peptide effect was unaffected by a membrane-permeable analog of cAMP. We conclude that CST and SST similarly increase K+ conductances in hippocampal neurons, most likely by activating SST receptors. However, CST additionally augments Ih, a voltage-dependent current that plays a key role in the modulation of synaptic integration and regulates oscillatory activity. Our results indicate that CST targets a specific conductance unaffected by SST to modulate cellular mechanisms implicated in sleep regulation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Somatostatin increases a voltage-insensitive K+ conductance in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 1998 Mar;79(3):1230-8. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.3.1230. J Neurophysiol. 1998. PMID: 9497404
-
Action of serotonin on the hyperpolarization-activated cation current (Ih) in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 1999 Sep;11(9):3093-100. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00728.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10510173
-
Theta-frequency membrane resonance and its ionic mechanisms in rat subicular pyramidal neurons.Neuroscience. 2006 Jun 19;140(1):45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.01.033. Epub 2006 Mar 9. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16527421
-
The role of neuropeptide somatostatin in the brain and its application in treating neurological disorders.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Mar;53(3):328-338. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00580-4. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33742131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cortistatin, a novel cardiovascular protective peptide.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2019 Aug;9(4):394-399. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2018.12.08. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2019. PMID: 31555545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CV. Somatostatin Receptors: Structure, Function, Ligands, and New Nomenclature.Pharmacol Rev. 2018 Oct;70(4):763-835. doi: 10.1124/pr.117.015388. Pharmacol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30232095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Somatostatin receptor 2 is activated in cortical neurons and contributes to neurodegeneration after focal ischemia.J Neurosci. 2004 Dec 15;24(50):11404-15. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3834-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15601946 Free PMC article.
-
Cortistatin-expressing interneurons require TrkB signaling to suppress neural hyper-excitability.Brain Struct Funct. 2019 Jan;224(1):471-483. doi: 10.1007/s00429-018-1783-1. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Brain Struct Funct. 2019. PMID: 30377803 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of the auxiliary subunit TRIP8b to HCN channels shifts the mode of action of cAMP.J Gen Physiol. 2013 Dec;142(6):599-612. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201311013. J Gen Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24277603 Free PMC article.
-
The fast and slow ups and downs of HCN channel regulation.Channels (Austin). 2010 May-Jun;4(3):215-31. doi: 10.4161/chan.4.3.11630. Channels (Austin). 2010. PMID: 20305382 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bickmeyer U, Heine M, Manzke T, Richter DW ( 2002) Differential modulation of Ih by 5-HT receptors in mouse CA1 hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 16: 209-218. - PubMed
-
- Braun H, Schulz S, Becker A, Schröder H, Höllt V ( 1998) Protective effects of cortistatin (CST-14) against kainate-induced neurotoxicity in rat brain. Brain Res 803: 54-60. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Gähwiler BH, Griffith WH, Halliwell JV ( 1990) Membrane currents in hippocampal neurons. Prog Brain Res 83: 141-160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
