Peptidergic nociceptors of both trigeminal and dorsal root ganglia express serotonin 1D receptors: implications for the selective antimigraine action of triptans
- PMID: 14645495
- PMCID: PMC6740979
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-34-10988.2003
Peptidergic nociceptors of both trigeminal and dorsal root ganglia express serotonin 1D receptors: implications for the selective antimigraine action of triptans
Abstract
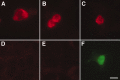
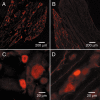
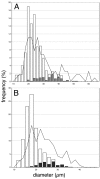
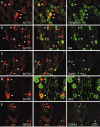
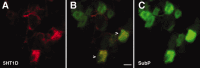
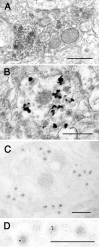
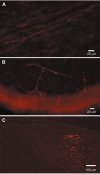
Agonists at serotonin 1D (5-HT1D) receptors relieve migraine headache but are not clinically used as general analgesics. One possible explanation for this difference is that 5-HT1D receptors are preferentially expressed by cranial afferents of the trigeminal system. We compared the distribution of 5-HT1D receptor-immunoreactive (5-HT1D-IR) peripheral afferents within the trigeminal ganglion (TRG) and lumbar dorsal root ganglion (DRG) of the rat. We also examined the neurochemical identity of 5-HT1D-IR neurons with markers of primary afferent nociceptors, peripherin, isolectin B4, and substance P, and markers of myelinated afferents, N52 and SSEA3. We observed a striking similarity in the size, distribution, and neurochemical identity of 5-HT1D-IR neurons in TRG and lumbar DRG afferents. Furthermore, the vast majority of 5-HT1D-IR neurons are unmyelinated peptidergic afferents that distribute peripherally, including the dura, cornea, and the sciatic nerve. In the central projections of these afferents within the trigeminal nucleus caudalis and the spinal cord dorsal horn, 5-HT1D-IR fibers are concentrated in laminas I and outer II; a few axons penetrate to lamina V. At the ultrastructural level, 5-HT1D receptors in the spinal cord dorsal horn are localized exclusively within dense core vesicles of synaptic terminals. We observed scattered 5-HT1D-IR neurons in the nodose ganglia, and there was sparse terminal immunoreactivity in the solitary nucleus. The visceral efferents of the superior cervical ganglia did not contain 5-HT1D immunoreactivity. Our finding, that 5-HT1D receptors are distributed in nociceptors throughout the body, raises the possibility that triptans can regulate not only headache-associated pain but also nociceptive responses in extracranial tissues.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Colocalization of CGRP with 5-HT1B/1D receptors and substance P in trigeminal ganglion neurons in rats.Eur J Neurosci. 2001 Jun;13(11):2099-104. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01586.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11422450
-
Distribution of 5-HT(1B), 5-HT(1D) and 5-HT(1F) receptor expression in rat trigeminal and dorsal root ganglia neurons: relevance to the selective anti-migraine effect of triptans.Brain Res. 2010 Nov 18;1361:76-85. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.09.004. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20833155
-
Tissue injury regulates serotonin 1D receptor expression: implications for the control of migraine and inflammatory pain.J Neurosci. 2006 Aug 9;26(32):8332-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1989-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16899728 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic Mouse Models for the Tracing of “Pain” Pathways.In: Kruger L, Light AR, editors. Translational Pain Research: From Mouse to Man. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2010. Chapter 7. In: Kruger L, Light AR, editors. Translational Pain Research: From Mouse to Man. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2010. Chapter 7. PMID: 21882471 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The science of migraine.J Vestib Res. 2011;21(6):305-14. doi: 10.3233/VES-2012-0433. J Vestib Res. 2011. PMID: 22348935 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional gene networks reveal distinct mechanisms segregating in migraine families.Brain. 2020 Oct 1;143(10):2945-2956. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa242. Brain. 2020. PMID: 32968778 Free PMC article.
-
Critical evaluation of the colocalization between calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance P, transient receptor potential vanilloid subfamily type 1 immunoreactivities, and isolectin B4 binding in primary afferent neurons of the rat and mouse.J Pain. 2007 Mar;8(3):263-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2006.09.005. Epub 2006 Nov 16. J Pain. 2007. PMID: 17113352 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin type 1D receptors (5HTR) are differentially distributed in nerve fibres innervating craniofacial tissues.Cephalalgia. 2008 Sep;28(9):933-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01635.x. Epub 2008 Jun 28. Cephalalgia. 2008. PMID: 18557979 Free PMC article.
-
Role of endothelial cells in antihyperalgesia induced by a triptan and β-blocker.Neuroscience. 2013 Mar 1;232:83-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.020. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23262231 Free PMC article.
-
Signals and switches in Mammalian neural crest cell differentiation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Feb 1;5(2):a008326. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008326. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23378583 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- al Balawi S, Tariq M, Feinmann C ( 1996) A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, study to evaluate the efficacy of subcutaneous sumatriptan in the treatment of atypical facial pain. Int J Neurosci 86: 301-309. - PubMed
-
- Amlaiky N, Ramboz S, Boschert U, Plassat JL, Hen R ( 1992) Isolation of a mouse “5HT1E-like” serotonin receptor expressed predominantly in hippocampus. J Biol Chem 267: 19761-19764. - PubMed
-
- Antonaci F, Pareja JA, Caminero AB, Sjaastad O ( 1998) Chronic paroxysmal hemicrania and hemicrania continua: lack of efficacy of sumatriptan. Headache 38: 197-200. - PubMed
-
- Bonaventure P, Voorn P, Luyten WH, Leysen JE ( 1998) 5HT1B and 5HT1D receptor mRNA differential co-localization with peptide mRNA in the guinea pig trigeminal ganglion. NeuroReport 9: 641-645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
