Nuclear factor I/thyroid transcription factor 1 interactions modulate surfactant protein C transcription
- PMID: 14645514
- PMCID: PMC309647
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.24.9014-9024.2003
Nuclear factor I/thyroid transcription factor 1 interactions modulate surfactant protein C transcription
Abstract
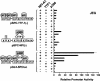
Surfactant protein C (SP-C; Sftpc) gene expression is restricted to pulmonary type II epithelial cells. The proximal SP-C promoter region contains critical binding sites for nuclear factor I (NFI) and thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1; also called Nkx2.1). To test the hypothesis that NFI isoforms interact with TTF-1 to differentially regulate SP-C transcription, we performed transient transfection assays in JEG-3 cells, a choriocarcinoma cell line with negligible endogenous NFI or TTF-1 activity. Cotransfection of NFI family members with TTF-1 induced synergistic activation of the SP-C promoter that was further enhanced by p300. TTF-1 directly interacts with the conserved DNA binding and dimerization domain of all NFI family members in coimmunoprecipitation and mammalian two-hybrid experiments. To determine whether SP-C expression is regulated by NFI in vivo, a chimeric fusion protein containing the DNA binding and dimerization domain of NFI-A and the Drosophila engrailed transcriptional repression domain (NFIen) was conditionally expressed in mice under control of a doxycycline-inducible transgene. Induction of NFIen in a subset of type II cells inhibited SP-C gene expression without affecting expression of TTF-1 in doxycycline-treated double-transgenic mice. Taken together, these findings support the hypothesis that NFI family members interact with TTF-1 to regulate type II cell function.
Figures
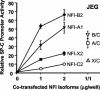
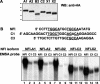
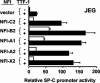
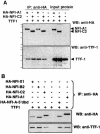
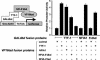
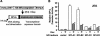
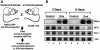
Similar articles
-
Thyroglobulin repression of thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1) gene expression is mediated by decreased DNA binding of nuclear factor I proteins which control constitutive TTF-1 expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Nov;20(22):8499-512. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.22.8499-8512.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11046146 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor I family members regulate the transcription of surfactant protein-C.J Biol Chem. 1997 Dec 26;272(52):32759-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.52.32759. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9407049
-
Erm/thyroid transcription factor 1 interactions modulate surfactant protein C transcription.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jun 16;281(24):16716-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602221200. Epub 2006 Apr 13. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16613858
-
The Nuclear Factor I (NFI) gene family in mammary gland development and function.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003 Apr;8(2):241-54. doi: 10.1023/a:1025909109843. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003. PMID: 14635798 Review.
-
Roles of the NFI/CTF gene family in transcription and development.Gene. 2000 May 16;249(1-2):31-45. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00140-2. Gene. 2000. PMID: 10831836 Review.
Cited by
-
NFIB overexpression cooperates with Rb/p53 deletion to promote small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):57514-57524. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11583. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27613844 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor gene Nfib is essential for both lung maturation and brain development.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;25(2):685-98. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.2.685-698.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15632069 Free PMC article.
-
Foxp2 inhibits Nkx2.1-mediated transcription of SP-C via interactions with the Nkx2.1 homeodomain.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Jun;38(6):750-8. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0350OC. Epub 2008 Jan 31. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18239190 Free PMC article.
-
FoxA1 and FoxA2 control growth and cellular identity in NKX2-1-positive lung adenocarcinoma.Dev Cell. 2022 Aug 8;57(15):1866-1882.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.06.017. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Dev Cell. 2022. PMID: 35835117 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Factor I/B: A Master Regulator of Cell Differentiation with Paradoxical Roles in Cancer.EBioMedicine. 2017 Aug;22:2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.05.027. Epub 2017 May 27. EBioMedicine. 2017. PMID: 28596133 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnone, M. I., M. Zannini, and R. Di Lauro. 1995. The DNA binding activity and the dimerization ability of the thyroid transcription factor I are redox regulated. J. Biol. Chem. 270:12048-12055. - PubMed
-
- Bachurski, C. J., S. E. Kelly, S. W. Glasser, and T. A. Currier. 1997. Nuclear factor I family members regulate the transcription of surfactant protein-C. J. Biol. Chem. 272:32759-32766. - PubMed
-
- Bachurski, C. J., G. S. Pryhuber, S. W. Glasser, S. E. Kelly, and J. A. Whitsett. 1995. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits surfactant protein C gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 270:19402-19407. - PubMed
-
- Bohinski, R. J., R. Di Lauro, and J. A. Whitsett. 1994. The lung-specific surfactant protein B gene promoter is a target for thyroid transcription factor 1 and hepatocyte nuclear factor 3, indicating common factors for organ-specific gene expression along the foregut axis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:5671-5681. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
