Characterization of Sleeping Beauty transposition and its application to genetic screening in mice
- PMID: 14645530
- PMCID: PMC309709
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.24.9189-9207.2003
Characterization of Sleeping Beauty transposition and its application to genetic screening in mice
Abstract
The use of mutant mice plays a pivotal role in determining the function of genes, and the recently reported germ line transposition of the Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon would provide a novel system to facilitate this approach. In this study, we characterized SB transposition in the mouse germ line and assessed its potential for generating mutant mice. Transposition sites not only were clustered within 3 Mb near the donor site but also were widely distributed outside this cluster, indicating that the SB transposon can be utilized for both region-specific and genome-wide mutagenesis. The complexity of transposition sites in the germ line was high enough for large-scale generation of mutant mice. Based on these initial results, we conducted germ line mutagenesis by using a gene trap scheme, and the use of a green fluorescent protein reporter made it possible to select for mutant mice rapidly and noninvasively. Interestingly, mice with mutations in the same gene, each with a different insertion site, were obtained by local transposition events, demonstrating the feasibility of the SB transposon system for region-specific mutagenesis. Our results indicate that the SB transposon system has unique features that complement other mutagenesis approaches.
Figures






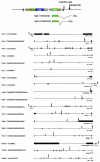
References
-
- Bellen, H. J., C. J. O'Kane, C. Wilson, U. Grossniklaus, R. K. Pearson, and W. J. Gehring. 1989. P-element-mediated enhancer detection: a versatile method to study development in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 3:1288-1300. - PubMed
-
- Bradley, A. 2002. Mining the mouse genome. Nature 420:512-514. - PubMed
-
- Brand, A. H., and N. Perrimon. 1993. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118:401-415. - PubMed
-
- Caubit, X., N. Core, A. Boned, S. Kerridge, M. Djabali, and L. Fasano. 2000. Vertebrate orthologues of the Drosophila region-specific patterning gene teashirt. Mech. Dev. 91:445-448. - PubMed
-
- Choi, J. W., S. Y. Lee, and Y. Choi. 1996. Identification of a putative G protein-coupled receptor induced during activation-induced apoptosis of T cells. Cell. Immunol. 168:78-84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
