Multiple promoters in the WNK1 gene: one controls expression of a kidney-specific kinase-defective isoform
- PMID: 14645531
- PMCID: PMC309643
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.24.9208-9221.2003
Multiple promoters in the WNK1 gene: one controls expression of a kidney-specific kinase-defective isoform
Abstract
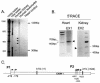
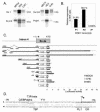
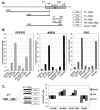
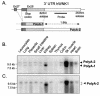
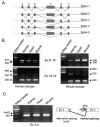
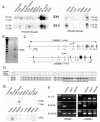
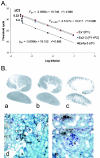
WNK1 is a serine-threonine kinase, the expression of which is affected in pseudohypoaldosteronism type II, a Mendelian form of arterial hypertension. We characterized human WNK1 transcripts to determine the molecular mechanisms governing WNK1 expression. We report the presence of two promoters generating two WNK1 isoforms with a complete kinase domain. Further variations are achieved by the use of two polyadenylation sites and tissue-specific splicing. We also determined the structure of a kidney-specific isoform regulated by a third promoter and starting at a novel exon. This transcript is kinase defective and has a predominant expression in the kidney compared to the other WNK1 isoforms, with, furthermore, a highly restricted expression profile in the distal convoluted tubule. We confirmed that the ubiquitous and kidney-specific promoters are functional in several cells lines and identified core promoters and regulatory elements. In particular, a strong enhancer element upstream from the kidney-specific exon seems specific to renal epithelial cells. Thus, control of human WNK1 gene expression of kinase-active or -deficient isoforms is mediated predominantly through the use of multiple transcription initiation sites and tissue-specific regulatory elements.
Figures

References
-
- Achard, J. M., D. G. Warnock, S. Disse-Nicodeme, B. Fiquet-Kempf, P. Corvol, A. Fournier, and X. Jeunemaitre. 2003. Familial hyperkalemic hypertension: phenotypic analysis in a large family with the WNK1 deletion mutation. Am. J. Med. 114:495-498. - PubMed
-
- Chomczynski, P., and N. Sacchi. 1987. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162:156-159. - PubMed
-
- Disse-Nicodeme, S., J. M. Achard, J. Potier, M. Delahousse, B. Fiquet-Kempf, N. Stern, A. Blanchard, J. C. Guilbaud, P. Niaudet, D. Chauveau, B. Dussol, Y. Berland, P. Dequiedt, J. L. Ader, M. Paillard, J. P. Grunfeld, A. Fournier, P. Corvol, and X. Jeunemaitre. 2001. Familial hyperkalemic hypertension (Gordon syndrome): evidence for phenotypic variability in a study of 7 families. Adv. Nephrol. Necker Hosp. 31:55-68. - PubMed
-
- Gordon, R. D., S. A. Klemm, T. J. Tunny, and M. Stowasser. 1995. Gordon's syndrome: a sodium-volume-dependent form of hypertension with a genetic basis, p. 2111-2123. In J. H. Laragh and B. M. Brenner (ed.), Hypertension: pathophysiology, diagnosis and management, 2nd ed. Raven Press, New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
