A stem structure in fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 transcripts mediates cell-type-specific splicing by approximating intronic control elements
- PMID: 14645542
- PMCID: PMC309649
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.24.9327-9337.2003
A stem structure in fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 transcripts mediates cell-type-specific splicing by approximating intronic control elements
Abstract
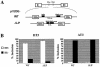
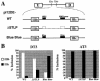
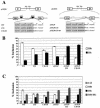
Alternative splicing of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) occurs in a cell-type-specific manner with the mutually exclusive use of exon IIIb or exon IIIc. Specific inclusion of exon IIIb is observed in epithelial cells, whereas exon IIIc inclusion is seen in mesenchymal cells. Epithelium-specific activation of exon IIIb and repression of exon IIIc are coordinately regulated by intronic activating sequence 2 (IAS2) and intronic splicing activator and repressor (ISAR) elements in FGFR2 pre-mRNA. Previously, it has been suggested that IAS2 and a 20-nucleotide core sequence of ISAR form a stem structure that allows for the proper regulation of FGFR2 alternative splicing. Replacement of IAS2 and the ISAR core with random sequences capable of stem formation resulted in the proper activation of exon IIIb and repression of exon IIIc in epithelial cells. Given the high degree of phylogenetic conservation of the IAS2-ISAR core structure and the fact that unrelated stem-forming sequences could functionally substitute for IAS2 and ISAR elements, we postulated that the stem structure facilitated the approximation of intronic control elements. Indeed, deletion of the entire stem-loop region and juxtaposition of sequences immediately upstream of IAS2 with sequences immediately downstream of the ISAR core maintained proper cell-type-specific inclusion of exon IIIb. These data demonstrate that IAS2 and the ISAR core are dispensable for the cell-type-specific activation of exon IIIb; thus, the major, if not the sole, role of the IAS2-ISAR stem in exon IIIb activation is to approximate sequences upstream of IAS2 with sequences downstream of the ISAR core. The downstream sequence is very likely a highly conserved GCAUG element, which we show was required for efficient exon IIIb activation.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed, Y. F., G. M. Gilmartin, S. M. Hanly, J. R. Nevins, and W. C. Greene. 1991. The HTLV-I Rex response element mediates a novel form of mRNA polyadenylation. Cell 64:727-737. - PubMed
-
- Brown, P. H., L. S. Tiley, and B. R. Cullen. 1991. Effect of RNA secondary structure on polyadenylation site selection. Genes Dev. 5:1277-1284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
