Differential roles of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in hypoxic gene regulation
- PMID: 14645546
- PMCID: PMC309606
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.24.9361-9374.2003
Differential roles of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in hypoxic gene regulation
Abstract
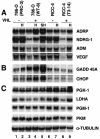
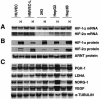
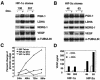
Transcriptional responses to hypoxia are primarily mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), a heterodimer of HIF-alpha and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator subunits. The HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha subunits are structurally similar in their DNA binding and dimerization domains but differ in their transactivation domains, implying they may have unique target genes. Previous studies using Hif-1alpha(-/-) embryonic stem and mouse embryonic fibroblast cells show that loss of HIF-1alpha eliminates all oxygen-regulated transcriptional responses analyzed, suggesting that HIF-2alpha is dispensable for hypoxic gene regulation. In contrast, HIF-2alpha has been shown to regulate some hypoxia-inducible genes in transient transfection assays and during embryonic development in the lung and other tissues. To address this discrepancy, and to identify specific HIF-2alpha target genes, we used DNA microarray analysis to evaluate hypoxic gene induction in cells expressing HIF-2alpha but not HIF-1alpha. In addition, we engineered HEK293 cells to express stabilized forms of HIF-1alpha or HIF-2alpha via a tetracycline-regulated promoter. In this first comparative study of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha target genes, we demonstrate that HIF-2alpha does regulate a variety of broadly expressed hypoxia-inducible genes, suggesting that its function is not restricted, as initially thought, to endothelial cell-specific gene expression. Importantly, HIF-1alpha (and not HIF-2alpha) stimulates glycolytic gene expression in both types of cells, clearly showing for the first time that HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha have unique targets.
Figures




References
-
- Alvarez-Tejado, M., S. Naranjo-Suarez, C. Jimenez, A. C. Carrera, M. O. Landazuri, and L. del Peso. 2001. Hypoxia induces the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt cell survival pathway in PC12 cells: protective role in apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 276:22368-22374. - PubMed
-
- Arsham, A. M., D. R. Plas, C. B. Thompson, and M. C. Simon. 2002. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling is neither required for hypoxic stabilization of HIF-1 alpha nor sufficient for HIF-1-dependent target gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 277:15162-15170. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay, R. S., M. Phelan, and D. V. Faller. 1995. Hypoxia induces AP-1-regulated genes and AP-1 transcription factor binding in human endothelial and other cell types. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1264:72-78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
