Varied immunity generated in mice by DNA vaccines with large and small hepatitis delta antigens
- PMID: 14645554
- PMCID: PMC296071
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.24.12980-12985.2003
Varied immunity generated in mice by DNA vaccines with large and small hepatitis delta antigens
Abstract
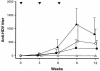
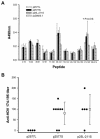
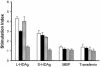
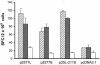
Whether the hepatitis delta virus (HDV) DNA vaccine can induce anti-HDV antibodies has been debatable. The role of the isoprenylated motif of hepatitis delta antigens (HDAg) in the generation of immune responses following DNA-based immunization has never been studied. Plasmids p2577L, encoding large HDAg (L-HDAg), p2577S, expressing small HDAg (S-HDAg), and p25L-211S, encoding a mutant form of L-HDAg with a cysteine-to-serine mutation at codon 211, were constructed in this study. Mice were intramuscularly injected with the plasmids. The anti-HDV antibody titers, T-cell proliferation responses, T-helper responses, and HDV-specific, gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-producing CD8(+) T cells were analyzed. Animals immunized with p2577S showed a strong anti-HDV antibody response. Conversely, only a low titer of anti-HDV antibodies was detected in mice immunized with p2577L. Epitope mapping revealed that the anti-HDV antibodies generated by p2577L vaccination hardly reacted with epitope amino acids 174 to 194, located at the C terminus of S-HDAg. All of the HDAg-encoding plasmids could induce significant T-cell proliferation responses and generate Th1 responses and HDV-specific, IFN-gamma-producing CD8(+) T cells. In conclusion, HDAg-specific antibodies definitely exist following DNA vaccination. The magnitudes of the humoral immune responses generated by L-HDAg- and S-HDAg-encoding DNA vaccines are different. The isoprenylated motif can mask epitope amino acids 174 to 195 of HDAg but does not interfere with cellular immunity following DNA-based immunization. These findings are important for the choice of a candidate HDV DNA vaccine in the future.
Figures



References
-
- Davey, S. 1996. State of the world's vaccines and immunization, p. 76-82. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Farci, P., A. Mandas, A. Colana, M. E. Lai, V. Desmet, P. Van Eyken, Y. Gibo, L. Caruso, S. Scaccabarozzi, D. Criscuolo, J. C. Ryff, and A. Balestrieri. 1994. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with interferon alfa-2a. N. Engl. J. Med. 330:88-94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

