The central region of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein contains distinct domains involved in subunit dimerization
- PMID: 14645559
- PMCID: PMC296077
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.24.13028-13035.2003
The central region of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein contains distinct domains involved in subunit dimerization
Abstract
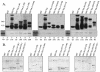
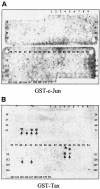
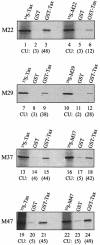
The Tax protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) can form homodimers. Tax dimerization contributes to optimal Tax activity involved in transactivation of the HTLV-1 promoter. The mechanisms used to form specific Tax dimers are poorly understood because the domains that mediate such interactions have not been clearly characterized. Here we have used different approaches (the two-hybrid assay in yeast, the glutathione S-transferase pull-down assay, and the Spot method) to study Tax-Tax interactions. Our results indicate that the integrity of the sequence of Tax, except for the last 16 amino acids (residues 338 to 353), is critical, suggesting that Tax dimerization is dictated more by secondary structure than by primary structure. We were, however, able to delimit a central region involved in Tax self-association that encompasses the residues 127 to 228. This region can be divided into three subdomains of dimerization: DD1 (residues 127 to 146), DD2 (residues 181 to 194), and DD3 (residues 213 to 228). Moreover, the Tax mutants M22 (T130A and L131S) and M29 (K189A and R190S), with amino acid substitutions located in DD1 and DD2, respectively, were found to be impaired in Tax self-association.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Interaction between HTLV-1 transcription activator tax and Taxreb107].Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai). 2002 Mar;34(2):231-5. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai). 2002. PMID: 12007002 Chinese.
-
Coiled-coil motif as a structural basis for the interaction of HTLV type 1 Tax with cellular cofactors.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Nov 1;16(16):1689-94. doi: 10.1089/08892220050193155. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 11080811
-
Tax relieves transcriptional repression by promoting histone deacetylase 1 release from the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(13):6735-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.13.6735-6743.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15194748 Free PMC article.
-
Human phospholipid scramblase 1 interacts with and regulates transactivation of HTLV-1 Tax.Virology. 2012 Oct 25;432(2):343-52. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.06.019. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Virology. 2012. PMID: 22789739
-
Hijacking of the O-GlcNAcZYME complex by the HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein facilitates viral transcription.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jul 24;13(7):e1006518. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006518. eCollection 2017 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28742148 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Intracellular localization and cellular factors interaction of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 Tax proteins: similarities and functional differences.Viruses. 2011 May;3(5):541-560. doi: 10.3390/v3050541. Epub 2011 May 9. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21994745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An interaction between the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 basic leucine zipper factor (HBZ) and the KIX domain of p300/CBP contributes to the down-regulation of tax-dependent viral transcription by HBZ.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 29;283(35):23903-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803116200. Epub 2008 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18599479 Free PMC article.
-
Functional comparison of antisense proteins of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 in viral pathogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2013 Aug 7;4:226. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00226. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23966985 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Genetic Organization, Expression Strategies and Oncogenic Potential of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2.Leuk Res Treatment. 2012;2012:876153. doi: 10.1155/2012/876153. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Leuk Res Treatment. 2012. PMID: 23213551 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV tax: a fascinating multifunctional co-regulator of viral and cellular pathways.Front Microbiol. 2012 Nov 30;3:406. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00406. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23226145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chun, A., Y. Zhou, C.-M. Wong, H.-K. Kung, K.-T. Jeang, and D.-Y. Jin. 2000. Coiled-coil motif as a structural basis for the interaction of HTLV type I Tax with cellular cofactors. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 16:1689-1694. - PubMed
-
- Frank, R. 1992. Spot-Sybthesis: an easy technique for the positionally addressable, parallel chemical synthesis on a membrane support. Tetrahedron 48:9217-9232.
-
- Franklin, A. A., and J. K. Nyborg. 1995. Mechanisms of Tax regulation of human T-cell leukemia virus type I gene expression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2:17-29. - PubMed
-
- Gachon, F., C. Devaux, and J. M. Mesnard. 2002. Activation of HTLV-1 transcription in the presence of Tax is independent of the acetylation of CREB-2 (ATF-4). Virology 299:271-278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

