Imaging Tetrahymena ribozyme splicing activity in single live mammalian cells
- PMID: 14645710
- PMCID: PMC299846
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2036553100
Imaging Tetrahymena ribozyme splicing activity in single live mammalian cells
Abstract
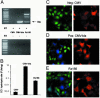
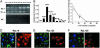
Tetrahymena ribozymes hold promise for repairing genetic disorders but are largely limited by their modest splicing efficiency and low production of final therapeutic proteins. Ribozyme evolution in intact living mammalian cells would greatly facilitate the discovery of new ribozyme variants with high in vivo activity, but no such strategies have been reported. Here we present a study using a new reporter enzyme, beta-lactamase, to report splicing activity in single living cells and perform high-throughput screening with flow cytometry. The reporter ribozyme constructs consist of the self-splicing Tetrahymena thermophila group I intron ribozyme that is inserted into the ORF of the mRNA of beta-lactamase. The splicing activity in single living cells can be readily detected quantitatively and visualized. Individual cells have shown considerable heterogeneity in ribozyme activity. Screening of Tetrahymena ribozymes with insertions in the middle of the L1 loop led to identification of better variants with at least 4-fold more final in vivo activity than the native sequence. Our work has provided a new reporter system that allows high-throughput screening with flow cytometry of single living mammalian cells for a direct and facile in vivo selection of desired ribozyme variants.
Figures
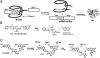


Similar articles
-
Single-cell detection of trans-splicing ribozyme in vivo activity.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Jun 16;126(23):7158-9. doi: 10.1021/ja049144u. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 15186136
-
Visualizing RNA splicing in vivo.Mol Biosyst. 2007 May;3(5):301-7. doi: 10.1039/b617574k. Epub 2007 Feb 21. Mol Biosyst. 2007. PMID: 17460789 Review.
-
Imaging target mRNA and siRNA-mediated gene silencing in vivo with ribozyme-based reporters.Chembiochem. 2008 Nov 3;9(16):2682-91. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200800370. Chembiochem. 2008. PMID: 18972511
-
Modulating the splicing activity of Tetrahymena ribozyme via RNA self-assembly.FEBS Lett. 2006 Mar 6;580(6):1592-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.01.090. Epub 2006 Feb 3. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 16472807
-
Biological and functional aspects of catalytic RNAs.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1992;2(4):331-57. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1992. PMID: 1486242 Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging of pre-mRNA splicing in living subjects using a genetically encoded luciferase reporter.Biomed Opt Express. 2018 Jan 8;9(2):518-528. doi: 10.1364/BOE.9.000518. eCollection 2018 Feb 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2018. PMID: 29552390 Free PMC article.
-
Flow cytometric detection of specific RNAs in native human cells with quenched autoligating FRET probes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jan 10;103(2):263-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509938103. Epub 2005 Dec 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16384914 Free PMC article.
-
A medaka model of cancer allowing direct observation of transplanted tumor cells in vivo at a cellular-level resolution.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 18;106(33):13832-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903999106. Epub 2009 Aug 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19666513 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive quantification of HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission in primary human CD4+ T cells measures viral sensitivity to broadly neutralizing antibodies.mBio. 2024 Jan 16;15(1):e0242823. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02428-23. Epub 2023 Dec 8. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38063394 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of melatonin by a whole cell bioassay in fermented beverages.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 24;9(1):9120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45645-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31235891 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

