Overexpression of a mutant basic helix-loop-helix protein HFR1, HFR1-deltaN105, activates a branch pathway of light signaling in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 14645731
- PMCID: PMC300719
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.029751
Overexpression of a mutant basic helix-loop-helix protein HFR1, HFR1-deltaN105, activates a branch pathway of light signaling in Arabidopsis
Abstract
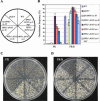
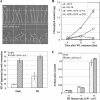
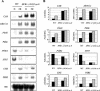
The HFR1, a basic helix-loop-helix protein, is required for a subset of phytochrome A-mediated photoresponses in Arabidopsis. Here, we show that overexpression of the HFR1-deltaN105 mutant, which lacks the N-terminal 105 amino acids, confers exaggerated photoresponses even in darkness. Physiological analysis implied that overexpression of HFR1-deltaN105 activated constitutively a branch pathway of light signaling that mediates a subset of photomorphogenic responses, including germination, de-etiolation, gravitropic hypocotyl growth, blocking of greening, and expression of some light-regulated genes such as CAB, DRT112, PSAE, PSBL, PORA, and XTR7, without affecting the light-responsiveness of anthocyanin accumulation and expression of other light-regulated genes such as CHS and PSBS. Although the end-of-day far-red light response and petiole elongation were suppressed in the HFR1-deltaN105-overexpressing plants, flowering time was not affected by HFR1-deltaN105. In addition, the HFR1-deltaN105-overexpressing plants showed hypersensitive photoresponses in the inhibition of hypocotyl elongation, dependently on phytochrome A, FHY1, and FHY3 under FR light or phyB under R light, respectively. Moreover, our double mutant analysis suggested that the hypersensitive photoresponse is due to functional cooperation between HFR1-deltaN105 and other light-signaling components including HY5, a basic leucine zipper protein. Taken together, our results of gain-of-function approach with HFR1-deltaN105 suggest the existence of a complex and important basic helix-loop-helix protein-mediated transcriptional network controlling a branch pathway of light signaling and provide a useful framework for further genetic dissection of light-signaling network in Arabidopsis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
HFR1, a phytochrome A-signalling component, acts in a separate pathway from HY5, downstream of COP1 in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J. 2002 Jun;30(6):711-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01326.x. Plant J. 2002. PMID: 12061902
-
Circadian-controlled basic/helix-loop-helix factor, PIL6, implicated in light-signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Physiol. 2004 Aug;45(8):1078-86. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pch124. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15356333
-
HFR1, a putative bHLH transcription factor, mediates both phytochrome A and cryptochrome signalling.Plant J. 2003 Jun;34(6):827-36. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01770.x. Plant J. 2003. PMID: 12795702
-
The shade avoidance syndrome in Arabidopsis: a fundamental role for atypical basic helix-loop-helix proteins as transcriptional cofactors.Plant J. 2011 Apr;66(2):258-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04485.x. Epub 2011 Feb 16. Plant J. 2011. PMID: 21205034
-
A network of interacting factors triggering different cell fates.Plant Cell. 2004 Sep;16(9):2258-63. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.160931. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15342905 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
PIL5, a phytochrome-interacting basic helix-loop-helix protein, is a key negative regulator of seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell. 2004 Nov;16(11):3045-58. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.025163. Epub 2004 Oct 14. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15486102 Free PMC article.
-
HFR1 is targeted by COP1 E3 ligase for post-translational proteolysis during phytochrome A signaling.Genes Dev. 2005 Mar 1;19(5):593-602. doi: 10.1101/gad.1247205. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15741320 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interconnections of HY1 with MYC2 and HY5 in Arabidopsis seedling development.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Mar 17;12:37. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-37. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 22424472 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of shade avoidance and auxin responses: a role for two novel atypical bHLH proteins.EMBO J. 2007 Nov 14;26(22):4756-67. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601890. Epub 2007 Oct 18. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17948056 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochrome signaling mechanisms and the control of plant development.Trends Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;21(11):664-71. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.07.002. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Trends Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21852137 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ang LH, Chattopadhyay S, Wei N, Oyama T, Okada K, Batschauer A, Deng XW (1998) Molecular interaction between COP1 and HY5 defines a regulatory switch for light control of Arabidopsis development. Mol Cell 1: 213-222 - PubMed
-
- Bechtold N, Ellis J, Pelletier G (1993) In planta Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. C R Acad Sci Paris Life Sci 316: 1194-1196
-
- Benvenuto G, Formiggini F, Laflamme P, Malakhov M, Bowler C (2002) The photomorphogenesis regulator DET1 binds the amino-terminal tail of histone H2B in a nucleosome context. Curr Biol 12: 1529-1534 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

