Matrix metalloproteinase-7 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 are associated with unfavourable prognosis in superficial oesophageal cancer
- PMID: 14647147
- PMCID: PMC2376843
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601372
Matrix metalloproteinase-7 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 are associated with unfavourable prognosis in superficial oesophageal cancer
Abstract
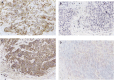
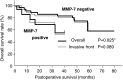
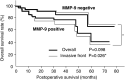
If oesophageal carcinoma is detected in the superficial stage, the prognosis is better than for advanced oesophageal carcinoma. But the factors which predict the prognosis and treatment policy remain unclear. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) have been reported to have close associations with tumour invasion and metastasis. In this study, we retrospectively studied the relations between MMP-7 and MMP-9 expression in immunohistochemistry, clinicopathologic factors, and prognosis in 55 superficial oesophageal carcinomas. MMP-7 and MMP-9 expression occurred in 23.6% and 47.3% of the patients, respectively. MMP-7 expression was significantly correlated with the presence of nodal metastasis (P=0.004). MMP-9 expression was significantly correlated with the depth of tumour invasion (P=0.004), lymphatic permeation (P=0.001), nodal metastasis (P=0.049), and pathologic differentiation grade (P=0.003). By the log-rank test, MMP-7 expression and MMP-9 expression on the invasive front were related to the prognosis. In multivariate analysis, MMP-9 expression on the invasive front was an independent prognostic indicator. The combined expression of MMP-7 and MMP-9 may be a good marker for the degree of malignancy of oesophageal cancer and for the presence of lymphatic metastasis.
Figures
References
-
- Adachi Y, Itoh F, Yamamoto H, Matsuno K, Arimura Y, Kusano M, Endoh T, Hinoda Y, Oohara M, Hosokawa M, Imai K (1998) Matrix metalloproteinase matrilysin (MMP-7) participates in the progression of human gastric and esophageal cancers. Int J Oncol 13: 1031–1035 - PubMed
-
- Adachi Y, Yamamoto H, Itoh F, Arimura Y, Nishi M, Endo T, Imai K (2001) Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of matrilysin expression at the invasive front in human colorectal cancers. Int J Cancer (Pred Oncol) 95: 290–294 - PubMed
-
- Baker EA, Leaper DJ (2002) Measuring gelatinase activity in colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 28: 24–29 - PubMed
-
- Baragi VM, Fliszar CJ, Conroy MC, Ye Q, Shipley JM, Welgus HG (1994) Contribution of the c-terminal domain of metalloproteinases to binding by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem 269: 12692–12697 - PubMed
-
- Bogomoletz WV, Molas G, Gayet B, Potet F (1989) Superficial squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a report of 76 cases and review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol 13: 535–546 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

