Irradiation differentially affects substratum-dependent survival, adhesion, and invasion of glioblastoma cell lines
- PMID: 14647148
- PMCID: PMC2376852
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601429
Irradiation differentially affects substratum-dependent survival, adhesion, and invasion of glioblastoma cell lines
Abstract
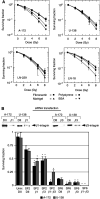
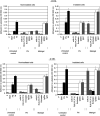
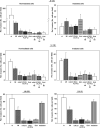
Effects of ionising radiation on extracellular matrix (ECM)-modulated cell survival and on adhesion and invasion are not well understood. In particular, the aggressiveness of glioblastoma multiforme has been associated with tumour cell invasion into adjacent normal brain tissue. To examine these effects in more depth, four human glioblastoma cell lines (A-172, U-138, LN-229 and LN-18) were irradiated on fibronectin (FN), Matrigel, BSA or polystyrene. Major findings of this study include a significantly increased survival of irradiated A-172 but not of irradiated U-138, LN-229, and LN-18 cells on FN or Matrigel compared to cells irradiated on polystyrene or BSA. Irradiation induced a dose-dependent increase in functional beta 1- and beta 3-integrins in all four glioma cell lines. This integrin induction caused improved cell adhesion to FN or Matrigel. In contrast to U-138, LN-229 and LN-18 cells, irradiation strongly impaired A-172 cell invasion. Invasion of all cell lines was inhibited by anti-integrin antibodies, the disintegrin echistatin and the MMP-2/-9 inhibitor III. Additionally, beta 1- and beta 3-integrins modulated basal and radiation-altered gelatinolytic activity of MMP-2. Tested glioblastoma cell lines showed a differential cellular susceptibility to FN or Matrigel which affected the cellular radiosensitivity. Three out of four glioma cell lines demonstrated a combination of a substratum-independent survival after irradiation and an invasive potential which was not affected by irradiation. beta 1- and beta 3-integrins were identified to play a substantial, regulatory role in survival, adhesion, invasion and MMP-2 activity. Detailed insights into radioresistance and invasion processes might offer new therapeutic strategies to enhance cell killing of lethal high-grade astrocytoma.
Figures




References
-
- Adams JC, Watt FM (1990) Changes in keratinocyte adhesion during terminal differentiation: reduction in fibronectin binding precedes alpha 5 beta 1 integrin loss from the cell surface. Cell 63: 425–435 - PubMed
-
- Albelda SM (1993) The role of integrins and other cell adhesion molecules in tumor progression and metastasis. Lab Invest 68: 4–17 - PubMed
-
- Ballin M, Gomez DE, Sinha CC, Thorgeirsson UP (1988) Ras oncogene mediated induction of a 92-kDa metalloproteinase: strong correlation with the malignant phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 154: 832–838 - PubMed
-
- Bauman GS, Fisher BJ, McDonald W, Amberger VR, Moore E, Del Maestro RF (1999) Effects of radiation on a three-dimensional model of malignant glioma invasion. Int J Dev Neurosci 17: 643–651 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

