Functional evaluation of the apoptosome in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 14647151
- PMCID: PMC2376849
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601436
Functional evaluation of the apoptosome in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
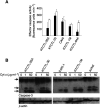
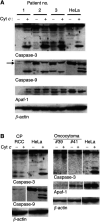
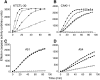
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) responds very poorly to chemo- or radiotherapy. Renal cell carcinoma cell lines have been described to be resistant to apoptosis-inducing stimuli and to lack caspase expression. Here, we provide a structural and functional assessment of the apoptosome, the central caspase-activating signalling complex and a candidate for apoptosis-inactivating mutations. Cells from RCC cell lines and clinical samples isolated from RCC patients were included. Apoptosome function was measured as quantitative activation of caspases in protein extracts. In all five cell lines and in 19 out of 20 primary clear cell RCC samples, the expression of apoptosome components and caspase activation appeared normal. Of the four nonclear cell RCC that could be included, both oncocytomas gave no response to cytochrome c (in one case, no Apaf-1 was detected), one chromophobe RCC lacked caspase-9 and failed to activate caspase-3 in response to cytochrome c, and one papillary RCC showed good caspase activation despite the lack of caspase-7. Experiments utilising a peptide derived from Smac/DIABLO gave no indication that inhibitor of apoptosis proteins might exert an inhibiting effect in primary clear cell RCC. Thus, the apoptosome signalling complex is intact in human (clear cell) RCC, and an apoptosis defect must be located at other, probably upstream, sites.
Figures
References
-
- Adams JM, Cory S (2001) Life-or-death decisions by the Bcl-2 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci 26: 61–66 - PubMed
-
- Arber N, Han EK, Sgambato A, Piazza GA, Delohery TM, Begemann M, Weghorst CM, Kim NH, Pamukcu R, Ahnen DJ, Reed JC, Weinstein IB, Holt PR (1997) A K-ras oncogene increases resistance to sulindac-induced apoptosis in rat enterocytes. Gastroenterology 113: 1892–1900 - PubMed
-
- Baker A, Payne CM, Briehl MM, Powis G (1997) Thioredoxin, a gene found overexpressed in human cancer, inhibits apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 57: 5162–5167 - PubMed
-
- Boer JM, Huber WK, Sultmann H, Wilmer F, von Heydebreck A, Haas S, Korn B, Gunawan B, Vente A, Fuzesi L, Vingron M, Poustka A (2001) Identification and classification of differentially expressed genes in renal cell carcinoma by expression profiling on a global human 31,500-element cDNA array. Genome Res 11: 1861–1870 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

