Potential involvement of the immune system in the development of endometriosis
- PMID: 14651748
- PMCID: PMC305339
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-1-123
Potential involvement of the immune system in the development of endometriosis
Abstract
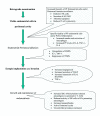
This article presents an overview of immunological factors and their role in the development of endometriosis, with emphasis on inflammatory cytokines, growth and adhesion factors. Although retrograde menstruation is a common phenomenon among women of reproductive age, not all women who have retrograde menstruation develop endometriosis. The development of endometriosis is hypothesised to be a complex process, which may be facilitated by several factors, including the quantity and quality of endometrial cells in peritoneal fluid (PF), increased inflammatory activity in PF, increased endometrial-peritoneal adhesion and angiogenesis, reduced immune surveillance and clearance of endometrial cells, and increased production of autoantibodies against endometrial cells. Potential biomarkers like cytokines and autoantibodies upregulated during development of endometriosis may be useful in the development of a non-surgical diagnostic tool. Although endometriosis can be treated using hormonal suppression, there is need for non-hormonal drugs, which can inhibit the development of endometriosis and alleviate pain or infertility without inhibition of ovulation. New molecules that modulate immune function in endometriosis should be the targets for future research.
Figures
References
-
- Guarnaccia M, Olive DL. The structure and future of endometriosis research. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1997;24:455–465. - PubMed
-
- Sampson JA. Peritoneal endometriosis due to menstrual dissemination of endometrial tissue into the peritoneal cavity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1927;14:422–469.
-
- Bartosik D, Jacobs SL, Kelly LJ. Endometrial tissue in peritoneal fluid. Fertil Steril. 1986;46:796–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical