Vaccines against sexually transmitted diseases
- PMID: 14651753
- PMCID: PMC305334
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-1-118
Vaccines against sexually transmitted diseases
Figures
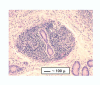

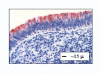
Similar articles
-
Venereal diseases of cattle: natural history, diagnosis, and the role of vaccines in their control.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2005 Jul;21(2):383-408. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2005.03.002. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2005. PMID: 15955436 Review. No abstract available.
-
Immunization in heifers with dual vaccines containing Tritrichomonas foetus and Campylobacter fetus antigens using systemic and mucosal routes.Theriogenology. 2004 Nov;62(8):1367-82. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2003.12.034. Theriogenology. 2004. PMID: 15451246
-
A review of sexually transmitted bovine trichomoniasis and campylobacteriosis affecting cattle reproductive health.Theriogenology. 2016 Mar 15;85(5):781-791. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2015.10.037. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Theriogenology. 2016. PMID: 26679515 Review.
-
Clearance of Tritrichomonas foetus in experimentally infected heifers protected with vaccines based on killed-T. foetus with different adjuvants.Vaccine. 2017 Mar 1;35(9):1341-1346. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.12.030. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Vaccine. 2017. PMID: 28185741
-
Vaccination studies for the control of campylobacteriosis in Jamaican cattle.Vet Rec. 1986 Sep 20;119(12):299-301. doi: 10.1136/vr.119.12.299. Vet Rec. 1986. PMID: 3776032
Cited by
-
Bovine neutrophils kill the sexually-transmitted parasite Tritrichomonas foetus using trogocytosis.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Apr;48(2):865-875. doi: 10.1007/s11259-023-10260-5. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 37968413 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of type strain Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis NCTC 10354T.J Bacteriol. 2011 Oct;193(20):5871-2. doi: 10.1128/JB.05854-11. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21952544 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Identification and Survey of Tetratrichomonas buttreyi and Pentatrichomonas hominis in Cattle in Shanxi Province, North China.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;15(13):1899. doi: 10.3390/ani15131899. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40646798 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative aspects of immunity and vaccination in human and bovine trichomoniasis: a review.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2016 Jan;48(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s11250-015-0909-1. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2016. PMID: 26424377 Review.
-
Time series analysis of bovine venereal diseases in La Pampa, Argentina.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 6;13(8):e0201739. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201739. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30080907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg RH, Firehammer BD, Border M, Myers LL. Effects of passively and actively acquired antibody on bovine campylobacteriosis (vibriosis) Am J Vet Res. 1979;40:21–25. - PubMed
-
- Corbeil LB, Winter AJ. Animal model for the study of genital immune mechanisms: Venereal vibriosis of cattle. In: Brooks GF, editor. Immunobiology of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Amer Soc Microbiol. Washington, DC; 1978. pp. 293–299.
-
- Corbeil LB, Schurig GG, Duncan JR, Wilkie BN, Winter AJ. Immunity in the female bovine reproductive tract based on the response to Campylobacter fetus. In: Butler JE, editor. The Ruminant Immune System. Adv Exp Med Biol. Vol. 137. Plenum Press; 1981. pp. 729–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

