Molecular genetic analysis of chloroplast gene promoters dependent on SIG2, a nucleus-encoded sigma factor for the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase, in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 14654684
- PMCID: PMC291874
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg935
Molecular genetic analysis of chloroplast gene promoters dependent on SIG2, a nucleus-encoded sigma factor for the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase, in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
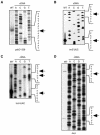
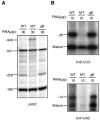
Most photosynthesis-related genes in mature chloroplasts are transcribed by a eubacterial-type RNA polymerase (PEP) whose core subunits are encoded by the plastid genome. It has been shown previously that six putative nuclear genes (SIG1 to SIG6) encode promoter-specificity factors for PEP in Arabidopsis thaliana, and we isolated a T-DNA insertion line of SIG2 (sig2-1 mutant) that manifests aberrant chloroplast development. With the use of S1 nuclease protection and primer extension analyses, we have now characterized the SIG2-dependent chloroplast promoters in A.thaliana. The amounts of transcripts derived from one of the multiple psbD promoters (psbD -256) and from the promoters of two tRNA genes (trnE-UUC and trnV-UAC) were markedly and specifically decreased in the sig2-1 mutant. The abundance of these transcripts was restored to wild-type levels by introduction into the mutant of a SIG2 transgene. The recombinant SIG2 protein mixed with Escherichia coli core RNA polymerase could bind to a DNA fragment that contains the SIG2-dependent psbD -256, trnE-UUC or trnV-UAC promoter. Sequences similar to those of the -35 and -10 promoter elements of E.coli were identified in the regions of the SIG2-dependent chloroplast genes upstream of the transcription initiation sites.
Figures


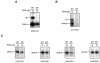



Similar articles
-
A nuclear-encoded sigma factor, Arabidopsis SIG6, recognizes sigma-70 type chloroplast promoters and regulates early chloroplast development in cotyledons.Plant J. 2005 Apr;42(2):133-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02362.x. Plant J. 2005. PMID: 15807777
-
An Arabidopsis sigma factor (SIG2)-dependent expression of plastid-encoded tRNAs in chloroplasts.Plant Cell Physiol. 2001 Oct;42(10):1034-43. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pce155. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11673617
-
Selective Activation of Chloroplast psbD Light-Responsive Promoter and psaA/B Promoter in Transplastomic Tobacco Plants Overexpressing Arabidopsis Sigma Factor AtSIG5.Protein Pept Lett. 2020;27(2):168-175. doi: 10.2174/0929866526666191014130605. Protein Pept Lett. 2020. PMID: 31612816
-
Roles of chloroplast RNA polymerase sigma factors in chloroplast development and stress response in higher plants.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2004 Nov;68(11):2215-23. doi: 10.1271/bbb.68.2215. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15564657 Review.
-
Chloroplast RNA polymerases: Role in chloroplast biogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Sep;1847(9):761-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25680513 Review.
Cited by
-
Plastid-to-nucleus retrograde signals are essential for the expression of nuclear starch biosynthesis genes during amyloplast differentiation in tobacco BY-2 cultured cells.Plant Physiol. 2011 Sep;157(1):518-30. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.178897. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21771917 Free PMC article.
-
Function of plastid sigma factors in higher plants: regulation of gene expression or just preservation of constitutive transcription?Plant Mol Biol. 2011 Jul;76(3-5):235-49. doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9714-4. Epub 2010 Nov 25. Plant Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21107995
-
High diversity of plastidial promoters in Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Genet Genomics. 2007 Jun;277(6):725-34. doi: 10.1007/s00438-007-0222-4. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Mol Genet Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17333279
-
AtSIG6, a plastid sigma factor from Arabidopsis, reveals functional impact of cpCK2 phosphorylation.Plant J. 2010 Apr;62(2):192-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04138.x. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 20088902 Free PMC article.
-
Plastid transcriptomics and translatomics of tomato fruit development and chloroplast-to-chromoplast differentiation: chromoplast gene expression largely serves the production of a single protein.Plant Cell. 2008 Apr;20(4):856-74. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.055202. Epub 2008 Apr 25. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18441214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sugita M. and Sugiura,M. (1996) Regulation of gene expression in chloroplasts of higher plants. Plant Mol. Biol., 32, 315–326. - PubMed
-
- Maliga P. (1998) Two plastid RNA polymerases of higher plants: an evolving story. Trends Plant Sci., 3, 4–6.
-
- Hess W.R. and Börner,T. (1999) Organellar RNA polymerases of higher plants. Int. Rev. Cytol., 190, 1–59. - PubMed
-
- Hedtke B., Börner,T. and Weihe,A. (1997) Mitochondrial and chloroplast phage-type RNA polymerases in Arabidopsis. Science, 277, 809–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

