A novel MALDI-TOF based methodology for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms
- PMID: 14654708
- PMCID: PMC291883
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gng156
A novel MALDI-TOF based methodology for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms
Abstract
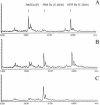
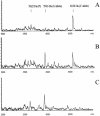
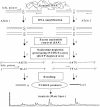
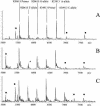
A new MALDI-TOF based detection assay was developed for analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). It is a significant modification on the classic three-step minisequencing method, which includes a polymerase chain reaction (PCR), removal of excess nucleotides and primers, followed by primer extension in the presence of dideoxynucleotides using modified thermostable DNA polymerase. The key feature of this novel assay is reliance upon deoxynucleotide mixes, lacking one of the nucleotides at the polymorphic position. During primer extension in the presence of depleted nucleotide mixes, standard thermostable DNA polymerases dissociate from the template at positions requiring a depleted nucleotide; this principal was harnessed to create a genotyping assay. The assay design requires a primer- extension primer having its 3'-end one nucleotide upstream from the interrogated site. The assay further utilizes the same DNA polymerase in both PCR and the primer extension step. This not only simplifies the assay but also greatly reduces the cost per genotype compared to minisequencing methodology. We demonstrate accurate genotyping using this methodology for two SNPs run in both singleplex and duplex reactions. We term this assay nucleotide depletion genotyping (NUDGE). Nucleotide depletion genotyping could be extended to other genotyping assays based on primer extension such as detection by gel or capillary electrophoresis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A new MALDI-TOF based mini-sequencing assay for genotyping of SNPS.Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jun 15;28(12):E68. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.12.e68. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 10871391 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex automated primer extension analysis: simultaneous genotyping of several polymorphisms.Biotechniques. 2001 Dec;31(6):1374-80. doi: 10.2144/01316md05. Biotechniques. 2001. PMID: 11768667
-
SNP genotyping using the Sequenom MassARRAY iPLEX platform.Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2009 Jan;Chapter 2:Unit 2.12. doi: 10.1002/0471142905.hg0212s60. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19170031
-
From gels to chips: "minisequencing" primer extension for analysis of point mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms.Hum Mutat. 1999;13(1):1-10. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1999)13:1<1::AID-HUMU1>3.0.CO;2-I. Hum Mutat. 1999. PMID: 9888384 Review.
-
Use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for multiplex genotyping.Adv Clin Chem. 2011;53:1-29. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-385855-9.00001-1. Adv Clin Chem. 2011. PMID: 21404912 Review.
Cited by
-
Proofreading and DNA Repair Assay Using Single Nucleotide Extension and MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Analysis.J Vis Exp. 2018 Jun 19;(136):57862. doi: 10.3791/57862. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 29985320 Free PMC article.
-
Uracil-DNA Glycosylase Assay by Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis.J Vis Exp. 2022 Apr 22;(182):10.3791/63089. doi: 10.3791/63089. J Vis Exp. 2022. PMID: 35532273 Free PMC article.
-
Candidate Genes from an FDA-Approved Algorithm Fail to Predict Opioid Use Disorder Risk in Over 450,000 Veterans.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 16:2024.05.16.24307486. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.16.24307486. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38798430 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Utility of Candidate Genes From an Algorithm Designed to Predict Genetic Risk for Opioid Use Disorder.JAMA Netw Open. 2025 Jan 2;8(1):e2453913. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.53913. JAMA Netw Open. 2025. PMID: 39786773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Risch N. and Merikangas,K. (1996) The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science, 273, 1516–1517. - PubMed
-
- Masood E. (1999) As consortium plans free SNP map of human genome. Nature, 398, 545–546. - PubMed
-
- Syvanen A.C., Aalto-Setala,K., Harju,L., Kontula,K. and Soderlund,H. (1990) A primer-guided nucleotide incorporation assay in the genotyping of apolipoprotein E. Genomics, 8, 684–692. - PubMed
-
- Pastinen T., Partanen,J. and Syvanen,A.C. (1996) Multiplex, fluorescent, solid-phase minisequencing for efficient screening of DNA sequence variation. Clin. Chem., 42, 1391–1397. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

