Penicillin for acute sore throat in children: randomised, double blind trial
- PMID: 14656841
- PMCID: PMC286321
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.327.7427.1324
Penicillin for acute sore throat in children: randomised, double blind trial
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effectiveness of penicillin for three days and treatment for seven days compared with placebo in resolving symptoms in children with sore throat.
Design: Randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial.
Setting: 43 family practices in the Netherlands.
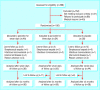
Participants: 156 children aged 4-15 who had a sore throat for less than seven days and at least two of the four Centor criteria (history of fever, absence of cough, swollen tender anterior cervical lymph nodes, and tonsillar exudate). Interventions Patients were randomly assigned to penicillin for seven days, penicillin for three days followed by placebo for four days, or placebo for seven days.
Main outcome measures: Duration of symptoms, mean consumption of analgesics, number of days of absence from school, occurrence of streptococcal sequelae, eradication of the initial pathogen, and recurrences of sore throat after six months.
Results: Penicillin treatment was not more beneficial than placebo in resolving symptoms of sore throat, neither in the total group nor in the 96 children with group A streptococci. In the groups randomised to seven days of penicillin, three days of penicillin, or placebo, one, two, and eight children, respectively, experienced a streptococcal sequela.
Conclusion: Penicillin treatment had no beneficial effect in children with sore throat on the average duration of symptoms. Penicillin may, however, reduce streptococcal sequelae.
Figures
Comment in
-
Penicillin for acute sore throat in children: randomised, double blind trial. Commentary: More valid criteria may be needed.BMJ. 2003 Dec 6;327(7427):1327-8. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7427.1327. BMJ. 2003. PMID: 14656842 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bisno AL, Gerber MA, Gwaltney JM Jr, Kaplan EL, Schwartz RH, Infectious Diseases Society of America. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis. Clin Infect Dis 2002;35: 113-25. - PubMed
-
- Del Mar CB, Glasziou PP, Spinks AB. Antibiotics for sore throat. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000;(4): CD000023. - PubMed
-
- Centor RM, Whitherspoon JM, Dalton HP, Brody ChE, Link K. The diagnosis of strep throat in adults in the emergency room. Med Decis Making 1981;1: 239-46. - PubMed
-
- Dagnelie CF, Zwart S, Balder FA, Romeijnders ACM, Geijer RMM. NHG Standard “Acute sore throat.” Utrecht: Dutch College of General Practitioners, 2002. http://nhg.artsennet.nl/guidelines2/E11.htm (accessed 21 Nov 2003).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical